Metabolic and Immune System Dysregulation: Unraveling the Connections between Alzheimer's Disease, Diabetes, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 39274269
- PMCID: PMC11396443
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13175057
Metabolic and Immune System Dysregulation: Unraveling the Connections between Alzheimer's Disease, Diabetes, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
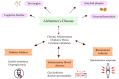
Alzheimer's disease (AD), diabetes mellitus (DM), inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are chronic conditions affecting millions globally. Despite differing clinical symptoms, these diseases share pathophysiological mechanisms involving metabolic and immune system dysregulation. This paper examines the intricate connections between these disorders, focusing on shared pathways such as insulin resistance, lipid metabolism dysregulation, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation. An important aspect is the role of amyloid-beta plaques and tau protein tangles, which are hallmark features of AD. These protein aggregates are influenced by metabolic dysfunction and inflammatory processes similar to those seen in DM, RA, and IBD. This manuscript explores how amyloid and tau pathologies may be exacerbated by shared metabolic and immune dysfunction. Additionally, this work discusses the gut-brain axis and the influence of gut microbiota in mediating disease interactions. Understanding these commonalities opens new avenues for multi-targeted therapeutic approaches that address the root causes rather than merely the symptoms of these conditions. This integrative perspective could lead to more effective interventions and improved patient outcomes, emphasizing the importance of a unified approach in managing these interconnected diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; diabetes mellitus; inflammatory bowel diseases; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
B.M. has received consultation and/or lecture honoraria from Abbott, Wiener, Roche, Cormay, Biameditek, and TK Biotech. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Carrero I., Gonzalo M.R., Martin B., Sanz-Anquela J.M., Arévalo-Serrano J., Gonzalo-Ruiz A. Oligomers of β-Amyloid Protein (Aβ1-42) Induce the Activation of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Astrocytes via an Interaction with Interleukin-1β, Tumour Necrosis Factor-α, and a Nuclear Factor κ-B Mechanism in the Rat Brain. Exp. Neurol. 2012;236:215–227. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.05.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources