The Impact of Standing Electric Scooters on Maxillofacial Fractures: An Italian Multi-Centric Epidemiological Study
- PMID: 39274410
- PMCID: PMC11395837
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13175195
The Impact of Standing Electric Scooters on Maxillofacial Fractures: An Italian Multi-Centric Epidemiological Study
Abstract
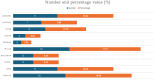
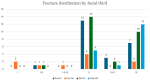
Objectives: This study aimed to determine the impact of standing electric scooters on maxillofacial on the Italian territory. Methods: The authors analyzed the epidemiology of the injuries to define electric mobility's impact on maxillofacial surgery practice. For this retrospective cohort study, data were collected by unifying the standing e-scooter-related fractures database from 10 Italian maxillofacial surgery departments. The reference period considered was from January 2020 to December 2023. The main data considered included age, gender, type of access, time slot of admission, type of admission, alcohol level, helmet use, dynamics of the accident, and area of the fracture. Results: A total of 79 patients were enrolled. The average age of the participants was approximately 31 years. The blood alcohol level was found to be above the Italian norm in 15 cases (19%). Only one patient wore a helmet. The most affected facial third was the middle one with 36 cases (45.5%), followed by the lower one (31, 39.3%). The most recurrent patterns were fractures of the orbito-malar-zygomatic complex (15, 19%), followed by multifocal (bifocal, trifocal) fractures of the mandible (14, 17.5%). Conclusions: This study demonstrated how maxillofacial fractures related to the use of electric scooters are associated with complex patterns, associated with a high rate of post-surgical aftermaths.
Keywords: craniofacial trauma; electric scooters; maxillofacial injury; traffic safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Roberta Fusco participated as the technical consultant for statistical analysis of the company Igea SpA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
E-Scooter-Related Maxillofacial Fractures: A New Emerging Epidemic During the COVID-19 Period in the Province of Rome, Lazio, Italy: A Monocentric Study Review of 843 Patients Compared With the Pre-COVID-19 Two-Year Period.J Craniofac Surg. 2024 Mar-Apr 01;35(2):510-514. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000009795. Epub 2023 Nov 2. J Craniofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 37916809
-
The impact of helmet use on oral and maxillofacial injuries associated with electric-powered bikes or powered scooter: a retrospective cross-sectional study.Head Face Med. 2021 Sep 1;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13005-021-00288-w. Head Face Med. 2021. PMID: 34470621 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of E-Scooter-Related Maxillofacial Injuries over 2019-2022-Retrospective Study from Poznan, Poland.J Clin Med. 2023 May 26;12(11):3690. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113690. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37297885 Free PMC article.
-
E-Scooters and Craniofacial Trauma: A Systematic Review.Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2023 Sep;16(3):245-253. doi: 10.1177/19433875221118790. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2023. PMID: 37975032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric electric scooter injuries in the UK: Case series and review of literature.Traffic Inj Prev. 2022;23(6):369-371. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2022.2084540. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Traffic Inj Prev. 2022. PMID: 35687112 Review.
References
-
- Gan-El E., Ngatchou Djomo W., Pascu Ciobanu A.M., Kaufman L., Ndé Djiélé F., Ulrix M., Kreps B., Plumacker A., Malinverni S., Bartiaux M., et al. Risk assessment, consequences, and epidemiology of electric scooter accidents admitted to an emergency department: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Trauma. Emerg. Surg. 2022;48:4847–4855. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-02019-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

