Risk Factors for Failure of Second-Trimester Termination with Misoprostol as a Single Agent
- PMID: 39274544
- PMCID: PMC11396749
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13175332
Risk Factors for Failure of Second-Trimester Termination with Misoprostol as a Single Agent
Abstract
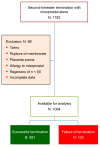
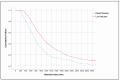
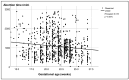
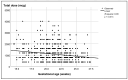
Background: Understanding the potential risk factors for failure of pregnancy termination is crucial for informed clinical decision making. Such insights can assist clinicians in adjusting the dosage or route of various regimens, as well as in counseling patients and predicting the likelihood of successful outcomes. However, research on these risk factors has been limited, and existing studies have yielded inconsistent results. To address this gap, we conducted a study with a large sample size, focusing on identifying the potential risk factors for failure of second-trimester termination using misoprostol as a single agent, specifically between 14 and 28 weeks of gestation. Methods: A secondary analysis based on a database of second-trimester terminations was conducted. The inclusion criteria were a singleton pregnancy, gestational age between 14 and 28 weeks, an unfavorable cervix, no spontaneous labor pain, intact membranes, and termination with misoprostol alone. Potential risk factors for failure of termination, defined as no abortion within 48 h, were analyzed using univariate and multivariate analyses. Results: A total of 1094 cases were included in the analysis, consisting of 991 successful cases and 103 (9.4%) cases of failure. The significant risk factors for failure of termination included early gestational age, live fetuses, sublingual regimen of 400 mcg every 6 h, and high maternal pre-pregnancy BMI. Previous cesarean sections and lower Bishop scores tended to increase the risk but did not reach a significant level. Conclusions: Second-trimester termination with misoprostol as a single agent was highly effective, with a failure rate of 9.4%. The risk factors for failure included gestational age, fetal viability, misoprostol regimen, and maternal pre-pregnancy BMI, suggesting that these factors should be taken into consideration for second-trimester terminations with misoprostol.
Keywords: abortion; failure of pregnancy termination; mid-pregnancy; misoprostol; risk factor; second trimester.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and adverse effects of vaginal misoprostol as a single agent for second trimester pregnancy termination: the impact of fetal viability.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 Apr;309(4):1459-1466. doi: 10.1007/s00404-023-07068-8. Epub 2023 May 6. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 37149516
-
Comparing the outcomes of termination of second trimester pregnancy with a live fetus using intravaginal misoprostol between women with and without previous cesarean section.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Apr 12;24(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06442-x. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38609883 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Pregnancy Termination of Dead Fetus in Utero in Second Trimester by Misoprostol with Various Regimens.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 3;19(19):12655. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912655. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231955 Free PMC article.
-
[Use of misoprostol for induction of labor in case of fetal death or termination of pregnancy during second or third trimester of pregnancy: Efficiency, dosage, route of administration, side effects, use in case of uterine scar].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2014 Feb;43(2):146-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2013.11.008. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2014. PMID: 24461423 Review. French.
-
Letrozole pretreatment prior to medical termination of pregnancy: a systematic review.Contraception. 2018 Jun;97(6):504-509. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Contraception. 2018. PMID: 29154779
References
-
- Al-Dughaishi T., Al-Jabri M.M.H., Al-Haddabi A.H., Gowri V. Trends of Patients’ Preferences in the Management of First and Early Second Trimester Pregnancy Loss Towards the Choice of Medical or Surgical Termination of Pregnancy in a Tertiary Care Center in Oman. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2019;20:52–56. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jacques L., Heinlein M., Ralph J., Pan A., Nugent M., Kaljo K., Farez R. Complication rates of dilation and evacuation and labor induction in second-trimester abortion for fetal indications: A retrospective cohort study. Contraception. 2020;102:83–86. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.04.018. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

