Pilose Antler Protein Relieves UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells and Skin Damage
- PMID: 39274908
- PMCID: PMC11397021
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29174060
Pilose Antler Protein Relieves UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells and Skin Damage
Abstract
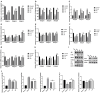
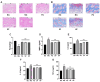
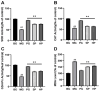
Extended exposure to UVB (280-315 nm) radiation results in oxidative damage and inflammation of the skin. Previous research has demonstrated that pilose antler extracts have strong anti-inflammatory properties and possess antioxidant effects. This study aimed to elucidate the mechanism of pilose antler protein in repairing photodamage caused by UVB radiation in HaCaT cells and ICR mice. Pilose antler protein (PAP) was found to increase the expression of type I collagen and hyaluronic acid in HaCaT cells under UVB irradiation while also inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and oxidative stress in vitro. In vivo, the topical application of pilose antler protein effectively attenuated UVB-induced skin damage in ICR mice by reducing interleukin-1β (IL-β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and inhibiting skin inflammation while alleviating UVB-induced oxidative stress. It was shown that pilose antler protein repaired UVB-induced photodamage through the MAPK and TGF-β/Smad pathways.
Keywords: HaCaT cells; UVB; pilose antler; skin damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Strakosha M., Vega-Mendoza D., Kane J., Jain A., Sun L., Rockowitz S., Elkins M., Miyake K., Chou J., Karasuyama H., et al. Basophils Play a Protective Role in the Recovery of Skin Barrier Function from Mechanical Injury in Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024;144:1784–1797. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.12.024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

