Ubiquitination and De-Ubiquitination in the Synthesis of Cow Milk Fat: Reality and Prospects
- PMID: 39274941
- PMCID: PMC11397273
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29174093
Ubiquitination and De-Ubiquitination in the Synthesis of Cow Milk Fat: Reality and Prospects
Abstract
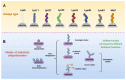
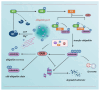
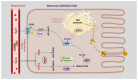
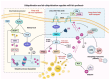
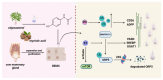
Ubiquitination modifications permit the degradation of labelled target proteins with the assistance of proteasomes and lysosomes, which is the main protein degradation pathway in eukaryotic cells. Polyubiquitination modifications of proteins can also affect their functions. De-ubiquitinating enzymes reverse the process of ubiquitination via cleavage of the ubiquitin molecule, which is known as a de-ubiquitination. It was demonstrated that ubiquitination and de-ubiquitination play key regulatory roles in fatty acid transport, de novo synthesis, and desaturation in dairy mammary epithelial cells. In addition, natural plant extracts, such as stigmasterol, promote milk fat synthesis in epithelial cells via the ubiquitination pathway. This paper reviews the current research on ubiquitination and de-ubiquitination in dairy milk fat production, with a view to providing a reference for subsequent research on milk fat and exploring new directions for the improvement of milk quality.
Keywords: de-ubiquitination; fatty acids; milk fat; proteasome; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The regulation of ubiquitination in milk fat synthesis in bovine].Yi Chuan. 2020 Jun 20;42(6):548-555. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-037. Yi Chuan. 2020. PMID: 32694113 Review. Chinese.
-
High expression of cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector a (CIDEA) promotes milk fat content in dairy cows with clinical ketosis.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Feb;102(2):1682-1692. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15439. Epub 2018 Dec 26. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30594378
-
The effects of cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor-α-like effector C (CIDEC) on milk lipid synthesis in mammary glands of dairy cows.J Dairy Sci. 2017 May;100(5):4014-4024. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11549. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Dairy Sci. 2017. PMID: 28284693
-
Identification and functional analysis of candidate gene VPS28 for milk fat in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Mar 19;510(4):606-613. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.01.016. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30739790
-
Invited review: palmitic and stearic acid metabolism in lactating dairy cows.J Dairy Sci. 2014;97(8):4661-74. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-7919. Epub 2014 Jun 7. J Dairy Sci. 2014. PMID: 24913651 Review.
Cited by
-
VPS28 regulates triglyceride synthesis via ubiquitination in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31310. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82774-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernard L., Leroux C., Chilliard Y. Expression and Nutritional Regulation of Lipogenic Genes in the Ruminant Lactating Mammary Gland. In: Bösze Z., editor. Bioactive Components of Milk. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2008. pp. 67–108. - PubMed
-
- Bullock J.B. Analysis of Milk Production Costs Using Cross-Section Data: The Problem of Converting Observed Quantities of Milk to a Standard Butterfat Content. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1971;53:323–324. doi: 10.2307/1237451. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

