Structure-Aided Computational Design of Triazole-Based Targeted Covalent Inhibitors of Cruzipain
- PMID: 39275072
- PMCID: PMC11396839
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29174224
Structure-Aided Computational Design of Triazole-Based Targeted Covalent Inhibitors of Cruzipain
Abstract
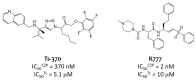
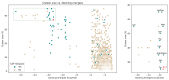
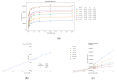
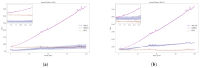
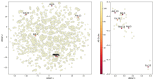
Cruzipain (CZP), the major cysteine protease present in T. cruzi, the ethiological agent of Chagas disease, has attracted particular attention as a therapeutic target for the development of targeted covalent inhibitors (TCI). The vast chemical space associated with the enormous molecular diversity feasible to explore by means of modern synthetic approaches allows the design of CZP inhibitors capable of exhibiting not only an efficient enzyme inhibition but also an adequate translation to anti-T. cruzi activity. In this work, a computer-aided design strategy was developed to combinatorially construct and screen large libraries of 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole analogues, further identifying a selected set of candidates for advancement towards synthetic and biological activity evaluation stages. In this way, a virtual molecular library comprising more than 75 thousand diverse and synthetically feasible analogues was studied by means of molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations in the search of potential TCI of CZP, guiding the synthetic efforts towards a subset of 48 candidates. These were synthesized by applying a Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) centered synthetic scheme, resulting in moderate to good yields and leading to the identification of 12 hits selectively inhibiting CZP activity with IC50 in the low micromolar range. Furthermore, four triazole derivatives showed good anti-T. cruzi inhibition when studied at 50 μM; and Ald-6 excelled for its high antitrypanocidal activity and low cytotoxicity, exhibiting complete in vitro biological activity translation from CZP to T. cruzi. Overall, not only Ald-6 merits further advancement to preclinical in vivo studies, but these findings also shed light on a valuable chemical space where molecular diversity might be explored in the search for efficient triazole-based antichagasic agents.
Keywords: Chagas disease; Cruzipain; computer-aided drug design; targeted covalent inhibitors; triazole derivatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

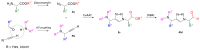

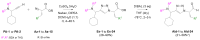
Similar articles
-
Synthesis, activity, and molecular modeling studies of 1,2,3-triazole derivatives from natural phenylpropanoids as new trypanocidal agents.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020 Jan;95(1):124-129. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13628. Epub 2019 Oct 20. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020. PMID: 31569301
-
Computer-aided design of 1,4-naphthoquinone-based inhibitors targeting cruzain and rhodesain cysteine proteases.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Jul 1;41:116213. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116213. Epub 2021 May 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33992862
-
Molecular Dynamics of a N-Cyclohexyl-1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivative as a Reversible Cruzain Inhibitor in Trypanosoma cruzi.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(19):2935-2939. doi: 10.2174/0113862073268297231025110913. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37957896
-
Cruzain inhibitors: efforts made, current leads and a structural outlook of new hits.Drug Discov Today. 2015 Jul;20(7):890-8. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Drug Discov Today. 2015. PMID: 25697479 Review.
-
The major cysteine proteinase of Trypanosoma cruzi: a valid target for chemotherapy of Chagas disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2001 Aug;7(12):1143-56. doi: 10.2174/1381612013397528. Curr Pharm Des. 2001. PMID: 11472258 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of novel compounds against Trypanosoma cruzi using AlphaFold structures.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 May 5;27:1838-1849. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.002. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40470316 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a Potent Triazole-Based Reversible Targeted Covalent Inhibitor of Cruzipain.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Dec 23;16(1):72-79. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00460. eCollection 2025 Jan 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39811116
-
Construction of Tandem Multimers with Different Combinatorial Forms of BmSPI38 and BmSPI39 and Analysis of Their Expression and Activity in Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 20;26(5):1788. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051788. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076416 Free PMC article.
-
Thiosulfonate-Based Targeted Covalent Cruzipain Inhibitors with Enhanced Bioactivity Translation for Antichagasic Therapy.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025 Feb 24;16(3):464-474. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00631. eCollection 2025 Mar 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40104787
-
Progress and Prospects of Triazoles in Advanced Therapies for Parasitic Diseases.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025 May 20;10(5):142. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed10050142. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40423371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Chagas Disease. [(accessed on 8 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/chagas-disease#tab=tab_1.
-
- World Health Organization . Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Roadmap for Implementation. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2012. Technical report.
-
- World Health Organization . Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals: A Sustainability Framework for Action Against Neglected Tropical Diseases 2021–2030. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021. Technical report.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

