Antihypertensive Effects of Lindera erythrocarpa Makino via NO/cGMP Pathway and Ca2+ and K+ Channels
- PMID: 39275318
- PMCID: PMC11397354
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16173003
Antihypertensive Effects of Lindera erythrocarpa Makino via NO/cGMP Pathway and Ca2+ and K+ Channels
Abstract
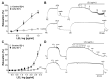
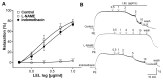
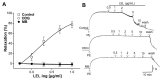
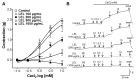
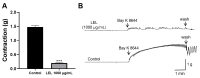
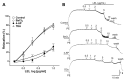
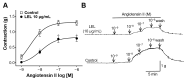
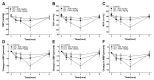
Studies have demonstrated the therapeutic effects of Lindera plants. This study was undertaken to reveal the antihypertensive properties of Lindera erythrocarpa leaf ethanolic extract (LEL). Aorta segments of Sprague-Dawley rats were used to study the vasodilatory effect of LEL, and the mechanisms involved were evaluated by treating specific inhibitors or activators that affect the contractility of blood vessels. Our results revealed that LEL promotes a vasorelaxant effect through the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate pathway, blocking the Ca2+ channels, opening the K+ channels, and inhibiting the vasoconstrictive action of angiotensin II. In addition, the effects of LEL on blood pressure were investigated in spontaneously hypertensive rats by the tail-cuff method. LEL (300 or 1000 mg/kg) was orally administered to the rats, and 1000 mg/kg of LEL significantly lowered the blood pressure. Systolic blood pressure decreased by -20.06 ± 4.87%, and diastolic blood pressure also lowered by -30.58 ± 5.92% at 4 h in the 1000 mg/kg LEL group. Overall, our results suggest that LEL may be useful to treat hypertensive diseases, considering its vasorelaxing and hypotensive effects.
Keywords: Lindera erythrocarpa; NO/cGMP pathway; angiotensin II; blood pressure; endothelium; hypertension; hypotensive effect; spontaneously hypertensive rat; vasorelaxant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Niiranen T.J., Lyass A., Larson M.G., Hamburg N.M., Benjamin E.J., Mitchell G.F., Vasan R.S. Prevalence, Correlates, and Prognosis of Healthy Vascular Aging in a Western Community-Dwelling Cohort: The Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 2017;70:267–274. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

