Life-Threatening tPA-Associated Angioedema: A Rare Case Report and Critical Review
- PMID: 39275799
- PMCID: PMC11409825
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.944221
Life-Threatening tPA-Associated Angioedema: A Rare Case Report and Critical Review
Abstract
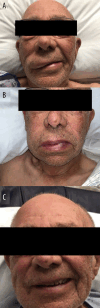
BACKGROUND Angioedema is characterized by localized self-limiting edema of the deep dermis, subcutaneous, and submucosal tissues. Acute episodes often involve the skin of the face, lips, tongue, limbs, and genitals, as well as internal areas of the body and respiratory and gastrointestinal mucosa, which could be life-threatening. Histamine and bradykinin are the most recognized vasoactive mediators in the pathophysiology of angioedema. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a fibrinolytic that is commonly used for the treatment of cerebrovascular accidents. Angioedema is a rare adverse effect of tPA, with an estimated incidence of 0.02% in patients with myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolism and 0.2% to 5.1% in patients with stroke. We report a unique case of tPA-associated angioedema with 24-h management. CASE REPORT A 79-year-old male patient presented to the Emergency Department with acute onset right-sided weakness, right-sided facial droop, and speech difficulties. Following the initial evaluation, it was determined that he was a candidate for receiving tPA therapy. On arrival at the Intensive Care Unit, he was noted to have right upper and then lower lip swelling. The patient was asymptomatic and did not show any signs concerning airway compromise. Treatment included systemic corticosteroids and antihistamines. The progression of the angioedema was further described with sequential images. The angioedema was completely resolved with treatment. CONCLUSIONS Angioedema is a rare but potentially life-threatening adverse effect of tPA. Although it generally has a mild self-limiting course, it can cause life-threatening airway compromise.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cicardi M, Aberer W, Banerji A, et al. Classification, diagnosis, and approach to treatment for angioedema: Consensus report from the Hereditary Angioedema International Working Group. Allergy. 2014;69(5):602–16. - PubMed
-
- Tsivgoulis G, Katsanos AH, Sandset EC, et al. Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke: Current status and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(5):418–29. - PubMed
-
- Jilani TN, Siddiqui AH. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Tissue plasminogen activator. [Updated 2023 Feb 20]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507917/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources