The ameliorative potential of metformin against aluminum-induced neurotoxicity: Insights from in vitro studies
- PMID: 39275926
- PMCID: PMC11738538
- DOI: 10.1002/jat.4695
The ameliorative potential of metformin against aluminum-induced neurotoxicity: Insights from in vitro studies
Abstract
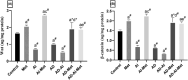
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is increasingly recognized as a metabolic disorder, often referred to as type 3 diabetes, due to its strong association with insulin resistance. Chronic exposure to aluminum, a known neurotoxin, has been identified as a significant risk factor in the development and progression of AD. This study explores the potential of metformin, a common anti-diabetic drug, to mitigate aluminum-induced neurotoxicity in an in vitro model of AD. Our findings reveal that metformin significantly reduces oxidative stress markers such as malonaldehyde, carbonyl groups, and reactive oxygen species while enhancing antioxidant defenses. Metformin modulates critical signaling pathways, including glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3-β)/RAC-alpha serine/threonine protein kinase (RAC-alpha serine/threonine protein kinase (Akt1)/protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and Wnt/β-catenin, decreasing Tau protein levels and promoting neurogenesis. These results suggest that metformin may offer a novel therapeutic approach for AD, particularly in cases where aluminum exposure is a contributing factor.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; GSK3‐β; Wnt signaling; aluminum; metformin.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Applied Toxicology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Agholme, L. , Lindström, T. , Kågedal, K. , Marcusson, J. , & Hallbeck, M. (2010). An in vitro model for neuroscience: Differentiation of SH‐SY5Y cells into cells with morphological and biochemical characteristics of mature neurons. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 20(4), 1069–1082. 10.3233/JAD-2010-091363 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barini, E. , Antico, O. , Zhao, Y. , Asta, F. , Tucci, V. , Catelani, T. , Marotta, R. , Xu, H. , & Gasparini, L. (2016). Metformin promotes tau aggregation and exacerbates abnormal behavior in a mouse model of tauopathy. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 11(1), 1–20. 10.1186/S13024-016-0082-7/FIGURES/6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basso, A. D. , Solit, D. B. , Chiosis, G. , Giri, B. , Tsichlis, P. , & Rosen, N. (2002). Akt forms an intracellular complex with heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and Cdc37 and is destabilized by inhibitors of Hsp90 function. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(42), 39858–39866. 10.1074/jbc.M206322200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

