Mei5-Sae3 stabilizes Dmc1 nucleating clusters for efficient Dmc1 assembly on RPA-coated single-stranded DNA
- PMID: 39275989
- PMCID: PMC11514449
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae780
Mei5-Sae3 stabilizes Dmc1 nucleating clusters for efficient Dmc1 assembly on RPA-coated single-stranded DNA
Abstract
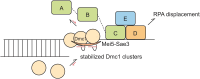
Interhomolog recombination in meiosis requires a meiosis-specific recombinase, Dmc1. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the Mei5-Sae3 complex facilitates the loading of Dmc1 onto the replication protein A (RPA)-coated single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to form nucleoprotein filaments. In vivo, Dmc1 and Mei5-Sae3 are interdependent in their colocalization on the chromosomes. However, the mechanistic role of Mei5-Sae3 in mediating Dmc1 activity remains unclear. We used single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer and colocalization single-molecule spectroscopy experiments to elucidate how Mei5-Sae3 stimulates Dmc1 assembly on ssDNA and RPA-coated ssDNA. We showed that Mei5-Sae3 stabilized Dmc1 nucleating clusters with two to three molecules on naked DNA by preferentially reducing Dmc1 dissociation rates. Mei5-Sae3 also stimulated Dmc1 assembly on RPA-coated DNA. Using green fluorescent protein-labeled RPA, we showed the coexistence of an intermediate with Dmc1 and RPA on ssDNA before RPA dissociation. Moreover, the displacement efficiency of RPA depended on Dmc1 concentration, and its dependence was positively correlated with the stability of Dmc1 clusters on short ssDNA. These findings suggest a molecular model that Mei5-Sae3 mediates Dmc1 binding on RPA-coated ssDNA by stabilizing Dmc1 nucleating clusters, thus altering RPA dynamics on DNA to promote RPA dissociation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Mei5-Sae3 protein complex mediates Dmc1 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 1;284(18):11766-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C900023200. Epub 2009 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19270307 Free PMC article.
-
A mutant form of Dmc1 that bypasses the requirement for accessory protein Mei5-Sae3 reveals independent activities of Mei5-Sae3 and Rad51 in Dmc1 filament stability.PLoS Genet. 2019 Dec 2;15(12):e1008217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008217. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31790385 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of Mei5, a subunit of Mei5-Sae3 complex, in Dmc1-mediated recombination during yeast meiosis.Genes Cells. 2024 Aug;29(8):650-666. doi: 10.1111/gtc.13138. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Genes Cells. 2024. PMID: 38924305
-
Homologous recombination: needing to have my say.Curr Biol. 2005 Mar 29;15(6):R200-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.03.009. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15797011 Review.
-
Chaperoning RPA during DNA metabolism.Curr Genet. 2019 Aug;65(4):857-864. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00945-3. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30796471 Review.
Cited by
-
SWI5-SFR1 reduces RAD51 recombinase extending units during filament assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 19;53(14):gkaf676. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf676. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40682818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ito M., Fujita Y., Shinohara A.. Positive and negative regulators of RAD51/DMC1 in homologous recombination and DNA replication. DNA Repair (Amst.). 2024; 134:103613. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

