The association between cigarette smoking and dementia with Lewy bodies
- PMID: 39276722
- PMCID: PMC11663461
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107133
The association between cigarette smoking and dementia with Lewy bodies
Abstract
Introduction: Cigarette smoking is associated with a reduced risk of Parkinson's disease (PD). As dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and PD share core neuropathologic features, we set out to examine the relationship between smoking and DLB.
Methods: Diagnosis at baseline visit and smoking history of participants ≥50 years old in the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center (NACC) cohort were evaluated in this cross-sectional study. Odds of diagnosis of cognitive impairment due to DLB, PD, vascular dementia (VD), or Alzheimer's disease (AD) compared to normal cognition based on smoking status and duration were determined using logistic regression.
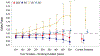
Results: 37,478 participants were included (mean age 72 years (SD 9), 57 % female). The odds of DLB were reduced in all smoking status groups compared to never smokers (OR (95 % CI)): ever smokers 0.850 (0.745-0.971), former smokers 0.871 (0.761-0.997), current smokers 0.640 (0.419-0.947)) and in all smoking duration groups. As expected, the odds of PD were reduced in all smoking groups and fell with longer smoking duration. The odds of VD were increased in the current smoking group and rose with greater smoking duration. The odds of AD were unchanged in current smokers, decreased in ever and former smokers, and increased with longer cumulative smoking duration.
Conclusions: Cigarette smoking is associated with lower odds of diagnosis of DLB at baseline visit in the NACC cohort. In the context of the well-established reduced risk of PD among smokers, this preliminary evidence of a potential protective effect of smoking on DLB warrants further study.
Keywords: Cigarette smoking; Dementia with Lewy bodies; National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Stephen Gomperts reports that financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with The Michael J Fox Foundation that includes: funding grants. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Farmer Family Foundation Parkinson's Research Initiative that includes: funding grants. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with US Office of Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs that includes: funding grants. Stephen Gomperts has patent #PCT/US20/36433 pending to Massachusetts General Hospital. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with EIP Pharma that includes: consulting or advisory and clinical trial work. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Hillhurst Biopharmaceuticals that includes: consulting or advisory and funding grants. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Biogen that includes: consulting or advisory. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Athenium Analytics that includes: consulting or advisory. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Clarivate Analytics US LLC that includes: consulting or advisory. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Guidepoint Global that includes: consulting or advisory. Stephen Gomperts reports a relationship with Cowen Group Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. Anna Gooheart declares that she has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA, The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: risk factors and prevention, Lancet Neurol 15(12) (2016) 1257–1272. - PubMed
-
- Grandinetti A, Morens DM, Reed D, MacEachern D, Prospective study of cigarette smoking and the risk of developing idiopathic Parkinson’s disease, Am J Epidemiol 139(12) (1994) 1129–38. - PubMed
-
- Hernan MA, Zhang SM, Rueda-deCastro AM, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Ascherio A, Cigarette smoking and the incidence of Parkinson’s disease in two prospective studies, Ann Neurol 50(6) (2001) 780–6. - PubMed
-
- Gorell JM, Rybicki BA, Johnson CC, Peterson EL, Smoking and Parkinson’s disease: a dose-response relationship, Neurology 52(1) (1999) 115–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P20 AG068053/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068082/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066518/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066512/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072978/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079280/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068024/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072958/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072931/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

