Inhibiting S-palmitoylation arrests metastasis by relocating Rap2b from plasma membrane in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 39277583
- PMCID: PMC11401852
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-07061-2
Inhibiting S-palmitoylation arrests metastasis by relocating Rap2b from plasma membrane in colorectal cancer
Abstract
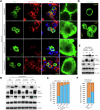
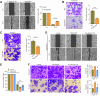
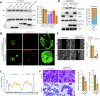
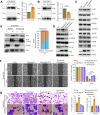
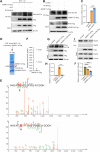
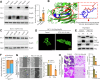
Rap2b, a proto-oncogene upregulated in colorectal cancer (CRC), undergoes protein S-palmitoylation at specific C-terminus sites (C176/C177). These palmitoylation sites are crucial for Rap2b localization on the plasma membrane (PM), as mutation of C176 or C177 results in cytosolic relocation of Rap2b. Our study demonstrates that Rap2b influences cell migration and invasion in CRC cells, independent of proliferation, and this activity relies on its palmitoylation. We identify ABHD17a as the depalmitoylating enzyme for Rap2b, altering PM localization and inhibiting cell migration and invasion. EGFR/PI3K signaling regulates Rap2b palmitoylation, with PI3K phosphorylating ABHD17a to modulate its activity. These findings highlight the potential of targeting Rap2b palmitoylation as an intervention strategy. Blocking the C176/C177 sites using an interacting peptide attenuates Rap2b palmitoylation, disrupting PM localization, and suppressing CRC metastasis. This study offers insights into therapeutic approaches targeting Rap2b palmitoylation for the treatment of metastatic CRC, presenting opportunities to improve patient outcomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JLZ and EYK are listed as inventors on pending patent covering the targeting of C176 and C177 in Rap2b as intervention strategy for treating cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Canobbio I, Trionfini P, Guidetti GF, Balduini C, Torti M. Targeting of the small GTPase Rap2b, but not Rap1b, to lipid rafts is promoted by palmitoylation at Cys176 and Cys177 and is required for efficient protein activation in human platelets. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1662–70. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.016 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

