Orientia tsutsugamushi Ank5 promotes NLRC5 cytoplasmic retention and degradation to inhibit MHC class I expression
- PMID: 39277599
- PMCID: PMC11401901
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52119-6
Orientia tsutsugamushi Ank5 promotes NLRC5 cytoplasmic retention and degradation to inhibit MHC class I expression
Abstract
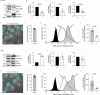
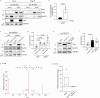
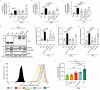
How intracellular bacteria subvert the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I pathway is poorly understood. Here, we show that the obligate intracellular bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi uses its effector protein, Ank5, to inhibit nuclear translocation of the MHC class I gene transactivator, NLRC5, and orchestrate its proteasomal degradation. Ank5 uses a tyrosine in its fourth ankyrin repeat to bind the NLRC5 N-terminus while its F-box directs host SCF complex ubiquitination of NLRC5 in the leucine-rich repeat region that dictates susceptibility to Orientia- and Ank5-mediated degradation. The ability of O. tsutsugamushi strains to degrade NLRC5 correlates with ank5 genomic carriage. Ectopically expressed Ank5 that can bind but not degrade NLRC5 protects the transactivator during Orientia infection. Thus, Ank5 is an immunoevasin that uses its bipartite architecture to rid host cells of NLRC5 and reduce surface MHC class I molecules. This study offers insight into how intracellular pathogens can impair MHC class I expression.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Orientia tsutsugamushi alters the intranuclear balance of cullin-1 and c-MYC to inhibit apoptosis.Infect Immun. 2025 Mar 11;93(3):e0055924. doi: 10.1128/iai.00559-24. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 39976440 Free PMC article.
-
The Obligate Intracellular Bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi Targets NLRC5 To Modulate the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Pathway.Infect Immun. 2019 Feb 21;87(3):e00876-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00876-18. Print 2019 Mar. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 30559222 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of Non-Ankyrin Repeat Domains of Orientia tsutsugamushi Ank Effectors Reveals Their Importance for Molecular Pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2022 May 19;90(5):e0062821. doi: 10.1128/iai.00628-21. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 35435726 Free PMC article.
-
Class I transactivator, NLRC5: a central player in the MHC class I pathway and cancer immune surveillance.Immunogenetics. 2019 Mar;71(3):273-282. doi: 10.1007/s00251-019-01106-z. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Immunogenetics. 2019. PMID: 30706093 Review.
-
MHC class I transactivator NLRC5 in host immunity, cancer and beyond.Immunology. 2021 Mar;162(3):252-261. doi: 10.1111/imm.13235. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 32633419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orientia tsutsugamushi modulates p53, the cell cycle, and genotoxicity to maintain its intracellular niche.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 19;16(1):7728. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-63149-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40830139 Free PMC article.
-
Orientia tsutsugamushi alters the intranuclear balance of cullin-1 and c-MYC to inhibit apoptosis.Infect Immun. 2025 Mar 11;93(3):e0055924. doi: 10.1128/iai.00559-24. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 39976440 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the structure domain and function of NLR family CARD domain containing 5.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jan 23;23(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-02012-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39849460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orientia tsutsugamushi Modulates RIPK3 Cellular Levels but Does Not Inhibit Necroptosis.Pathogens. 2025 May 14;14(5):478. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14050478. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40430799 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1F32 AI174656A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- 1R01 AI167857/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
- 1R01 AI123346/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- 2R56 AI123346/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R56 AI123346/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

