TUBB4B is essential for the cytoskeletal architecture of cochlear supporting cells and motile cilia development
- PMID: 39277687
- PMCID: PMC11401917
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06867-2
TUBB4B is essential for the cytoskeletal architecture of cochlear supporting cells and motile cilia development
Abstract
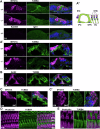
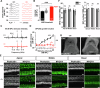
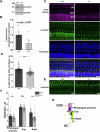
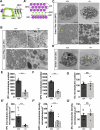
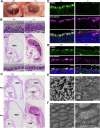
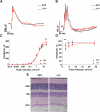
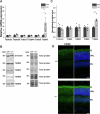
Microtubules are essential for various cellular processes. The functional diversity of microtubules is attributed to the incorporation of various α- and β-tubulin isotypes encoded by different genes. In this work, we investigated the functional role of β4B-tubulin isotype (TUBB4B) in hearing and vision as mutations in TUBB4B are associated with sensorineural disease. Using a Tubb4b knockout mouse model, our findings demonstrate that TUBB4B is essential for hearing. Mice lacking TUBB4B are profoundly deaf due to defects in the inner and middle ear. Specifically, in the inner ear, the absence of TUBB4B lead to disorganized and reduced densities of microtubules in pillar cells, suggesting a critical role for TUBB4B in providing mechanical support for auditory transmission. In the middle ear, Tubb4b-/- mice exhibit motile cilia defects in epithelial cells, leading to the development of otitis media. However, Tubb4b deletion does not affect photoreceptor function or cause retinal degeneration. Intriguingly, β6-tubulin levels increase in retinas lacking β4B-tubulin isotype, suggesting a functional compensation mechanism. Our findings illustrate the essential roles of TUBB4B in hearing but not in vision in mice, highlighting the distinct functions of tubulin isotypes in different sensory systems.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01EY031346/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R01 DC021835/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY031346/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM144230/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM138023/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35 GM138023/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY024280/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- P20GM144230/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 EY024280/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM133369/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- T32 GM133369/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY028035/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R01 EY028035/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM132494/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DC019195/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM132494/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

