Crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints: a systematic review of clinical features, diagnosis, management, and outcomes
- PMID: 39277771
- PMCID: PMC11401381
- DOI: 10.1186/s41927-024-00411-9
Crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints: a systematic review of clinical features, diagnosis, management, and outcomes
Abstract
Background: To summarize clinical presentations, baseline characteristics, diagnosis, treatment, and treatment outcomes through a systematic review of cases of crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints in the literature.
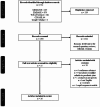
Methods: A systematic review of case reports and case series was performed according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. A literature search was performed through PubMed/MEDLINE, Google Scholar, Embase, Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health, and Web of Science. We identified case reports/case series in English of adult patients presenting with crystal-induced arthritis (gout, calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease) in prosthetic joints. Articles that met the inclusion criteria were utilized for qualitative data synthesis.
Results: We found 44 cases of crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints from 1984 to 2021. Crystal-induced arthritis in periprosthetic joints most frequently affects patients who had knee arthroplasty and most often presents as monoarticular arthritis that is usually acute in onset. However, several cases in the literature involved patients who had bilateral knee replacements and presented with a concurrent flare of gout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease in bilateral knees. Patients with crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints show elevated white blood cell counts with neutrophil predominance and respond favorably to anti-inflammatory treatments, usually within one week. In many cases, crystal-induced arthritis was challenging to differentiate from prosthetic joint infection, with approximately one-third of patients undergoing surgical intervention and 35% receiving antibiotic treatment.
Conclusion: Crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints can mimic prosthetic joint infections and should always be considered in the differential diagnoses of joint pain in prosthetic joints. We present the first systematic review of crystal-induced arthritis in prosthetic joints to increase awareness of the diagnosis and proper management.
Keywords: Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease; Crystal-induced arthritis; Gout; Prosthetic joints.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
-
- Prior-Espanol A, Garcia-Mira Y, Minguez S, Martinez-Morillo M, Gifre L, Mateo L. Coexistence of septic and crystal-induced arthritis: a diagnostic challenge. A report of 25 cases. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2019;15:e81–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous