Therapeutic efficacy of compound organic acids administration on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced arthritis in broilers
- PMID: 39278110
- PMCID: PMC11419824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104219
Therapeutic efficacy of compound organic acids administration on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced arthritis in broilers
Abstract
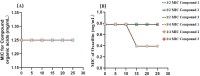
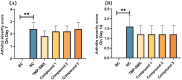
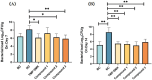
Avian arthritis is a common disease in the poultry industry, and the etiology is complex. Bacterial arthritis is usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection. This study explored the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of different organic acids against S. aureus MRSA85 and found that vanillic acid, suberic acid, itaconic acid, salicylic acid, and other organic acids had significant inhibitory effects on this strain, especially cinnamic acid, which exhibited the best inhibitory effect. The Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index (FICI) test further revealed the synergistic effect among some compound organic acids, which can significantly enhance the antibacterial efficiency against MRSA85 while reducing the risk of bacterial resistance. Under the low concentrations (1/2 or 1/4 MIC) conditions, the MIC of the compound organic acids against S. aureus remains unchanged, and it can even enhance the sensitivity of antibiotic-resistant S. aureus to Oxacillin. Furthermore, the compound organic acids could effectively promote the recovery of S. aureus-induced arthritis in broiler models, reduce inflammatory responses, and lower down bacterial loads and inflammatory cytokine levels in joints, which indicated that the effects of the Compound 2 is comparable to that of the trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole group. These results support the potential and application value of organic acids and their compounds, including Compound 1 to 3, as novel antibacterial agents in the treatment of S. aureus infections.
Keywords: MRSA; Staphylococcus aureus; arthritis; broiler; organic acid.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Triterpenoid saponin from Panax ginseng increases the sensitivity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to β-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0322723. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03227-23. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38647286 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to Anti-Inflammatory Drugs with a Focus on the Combinatory Effect of Celecoxib with Oxacillin In Vitro.Molecules. 2024 Aug 2;29(15):3665. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153665. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125072 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in poultry.Emerg Infect Dis. 2009 Mar;15(3):452-3. doi: 10.3201/eid1503.080696. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19239762 Free PMC article.
-
Cleistochlamys kirkii chemical constituents: Antibacterial activity and synergistic effects against resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 3;178:180-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26674158
-
Synergistic antibacterial effects of herbal extracts and antibiotics on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A computational and experimental study.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Apr;242(7):731-743. doi: 10.1177/1535370216689828. Epub 2017 Jan 1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28118725 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the antibacterial and anti-biofilm properties of Diacerein against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 20;16:1545902. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1545902. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40182283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai R., Miao M., Yue T., Zhang Y., Cui L., Wang Z., Yuan Y. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamic acid and chlorogenic acid against alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells in apple juice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019;54:1697–1705.
-
- Cao J.R., Fu H.J., Gao L.H., Zheng Y. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of lactobionic acid against. Folia. Microbiol. 2019;64:899–906. - PubMed
-
- Fouilloux J., Abbad-Andaloussi S., Langlois V., Dammak L., Renard E. Green physical modification of polypropylene fabrics by cross-linking chitosan with tannic acid and postmodification by quaternary ammonium grafting to improve antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2023;6:5609–5620. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

