A Pooled Analysis of Eight Clinical Studies Suggests a Link Between Influenza-Like Symptoms and Pharmacodynamics of the Toll-Like Receptor-7 Agonist Vesatolimod
- PMID: 39278975
- PMCID: PMC11499514
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-024-01034-w
A Pooled Analysis of Eight Clinical Studies Suggests a Link Between Influenza-Like Symptoms and Pharmacodynamics of the Toll-Like Receptor-7 Agonist Vesatolimod
Abstract
Introduction: Vesatolimod is a Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR7) agonist in clinical development as part of a combination regimen for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) cure. Influenza-like symptoms associated with TLR7-mediated immune activation have been reported in clinical trials of vesatolimod. Therefore, a broader understanding of the safety profile of vesatolimod and association with dose and mechanism of action will help inform future clinical studies.
Methods: In this analysis, data on flu-like adverse events of interest (AEIs) were pooled from eight clinical studies in which 606 participants either received single or multiple doses of vesatolimod (0.3-12 mg; n = 505) or placebo (n = 101). Vesatolimod pharmacokinetics, inflammatory responses, and pharmacodynamics were assessed.
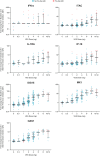
Results: The incidence of flu-like AEIs was higher with vesatolimod versus placebo (19% [96/505] vs. 8% [8/101]) and increased with vesatolimod dose and exposure. Most flu-like AEIs with vesatolimod were grade 1 or 2 severity (55% [53 of 96] grade 1; 35% [34 of 96] grade 2) with onset primarily after the first and second dose. Occurrence of flu-like AEIs after doses 1-3 was predictive of reoccurrence after later doses. Dose-dependent elevations of pharmacodynamic biomarkers (interferon-stimulated gene 15, 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 1, myxovirus resistance-1, interferon-α, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, interferon-γ-induced protein 10, interferon-inducible T-cell-α chemoattractant) observed in participants with flu-like AEIs suggest a link with vesatolimod mechanism of action.
Conclusions: Flu-like AEIs associated with vesatolimod administration were typically mild but increased with exposure, which may be predicted by the response to initial doses. The data suggest that adaptive clinical monitoring could help maximize pharmacodynamic responses and balance adverse events in future clinical trials of vesatolimod.
Keywords: Influenza-like adverse events; Safety; Toll-like receptor-7 agonist; Vesatolimod.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Sharon A. Riddler reports grants from Gilead and NIH/NIAID during the conduct of the study, as well as a grant from Merck outside the submitted work. Constance A. Benson reports grants from Gilead and NIH/NIAID during the conduct of the study and honoraria for educational lectures and personal fees for meeting travel from the IAS-USA, and has held leadership positions on the IAS-USA Board and the CROI Foundation Board. Cynthia Brinson is on the Speaker’s Bureau for Gilead and reports personal fees from Gilead for meeting travel. Steven G. Deeks reports grants from Gilead, consulting fees from AbbVie, GlaxoSmithKline, Hookipa, and Immunocore, and stock or stock options in BryoLogyx, Enochian BioSciences, and Trendel. Anthony Mills and Michael F. Para declare no competing interests. Edwin DeJesus reports grants and speaker and/or advisory fees from Gilead, Janssen, Abbott, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sangamo, TaiMed, Theraco Technologies, Vertex and ViiV Healthcare, both during the conduct of the study and outside the submitted work. Moti N. Ramgopal reports consulting fees and/or honoraria from Gilead, AbbVie, Janssen, ViiV Healthcare, and Merck. Yanhui Cai, Yanan Zheng, Liao Zhang, Wendy Jiang, Xiaopeng Liu, Donovan Verrill, Daina Lim, Christiaan R. de Vries, Jeffrey J. Wallin, Elena Vendrame, and Devi SenGupta are employees and shareholders of Gilead.
Figures


References
-
- Lawitz E, Gruener D, Marbury T, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral Toll-like receptor-7 agonist GS-9620 in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther. 2015;20(7):699–708. - PubMed
-
- Lopatin U, Wolfgang G, Tumas D, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of GS-9620, an oral Toll-like receptor-7 agonist. Antivir Ther. 2013;18(3):409–18. - PubMed
-
- Riddler SA, Para M, Benson CA, et al. Vesatolimod, a Toll-like receptor-7 agonist, induces immune activation in virally suppressed adults living with human immunodeficiency virus-1. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72(11):e815–24. - PubMed
-
- Janssen HLA, Brunetto MR, Kim YJ, et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2018;68(3):431–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

