Neoadjuvant nivolumab and relatlimab in locally advanced MMR-deficient colon cancer: a phase 2 trial
- PMID: 39278994
- PMCID: PMC11564102
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03250-w
Neoadjuvant nivolumab and relatlimab in locally advanced MMR-deficient colon cancer: a phase 2 trial
Abstract
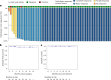
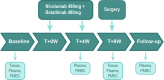
Mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) is found in approximately 15% of non-metastatic colon cancers (CCs) and is characterized by a defective DNA mismatch repair system, resulting in hypermutated and highly immunogenic tumors. Although patients with dMMR CC have limited benefit from chemotherapy, these tumors have been shown to respond exceptionally well to neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 plus anti-CTLA-4, with high rates of pathologic responses. Here, based on data from melanoma studies, we postulated a high efficacy and favorable toxicity profile of anti-PD-1 plus anti-LAG-3. In the NICHE-3 study, a total of 59 patients with locally advanced dMMR CC were treated with two 4-weekly cycles of nivolumab (480 mg) plus relatlimab (480 mg) before surgery. Pathologic response was observed in 57 of 59 (97%; 95% confidence interval (CI): 88-100%) patients, meeting the primary endpoint. Responses included 54 (92%; 95% CI: 81-97%) major pathologic responses (≤10% residual viable tumor) and 40 (68%; 95% CI: 54-79%) pathologic complete responses. With a median follow-up of 8 months (range, 2-19), one patient had recurrence of disease. The treatment displayed an acceptable safety profile, with all-grade and grade 3-4 immune-related adverse events (irAEs) occurring in 80% and 10% of patients, respectively. The most common irAEs were infusion-related reactions (29%), thyroid dysfunction (22%) and fatigue (20%). In conclusion, our results show that neoadjuvant nivolumab/relatlimab induces high rates of pathologic responses and that further investigation of this treatment in larger studies is warranted. These data add to the body of evidence in support of neoadjuvant immunotherapy regimens in dMMR CC. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03026140 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cervantes, A. et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol.34, 10–32 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Andre, T. et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.383, 2207–2218 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Kelly, R. J. et al. Adjuvant nivolumab in resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.384, 1191–1203 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Schmid, P. et al. Pembrolizumab for early triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.382, 810–821 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

