Epigenetic Dynamics in Reprogramming to Dopaminergic Neurons for Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 39279468
- PMCID: PMC11538697
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202403105
Epigenetic Dynamics in Reprogramming to Dopaminergic Neurons for Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
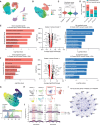
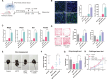
Direct lineage reprogramming into dopaminergic (DA) neurons holds great promise for the more effective production of DA neurons, offering potential therapeutic benefits for conditions such as Parkinson's disease. However, the reprogramming pathway for fully reprogrammed DA neurons remains largely unclear, resulting in immature and dead-end states with low efficiency. In this study, using single-cell RNA sequencing, the trajectory of reprogramming DA neurons at multiple time points, identifying a continuous pathway for their reprogramming is analyzed. It is identified that intermediate cell populations are crucial for resetting host cell fate during early DA neuronal reprogramming. Further, longitudinal dissection uncovered two distinct trajectories: one leading to successful reprogramming and the other to a dead end. Notably, Arid4b, a histone modifier, as a crucial regulator at this branch point, essential for the successful trajectory and acquisition of mature dopaminergic neuronal identity is identified. Consistently, overexpressing Arid4b in the DA neuronal reprogramming process increases the yield of iDA neurons and effectively reverses the disease phenotypes observed in the PD mouse brain. Thus, gaining insights into the cellular trajectory holds significant importance for devising regenerative medicine strategies, particularly in the context of addressing neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; cellular trajectory; direct reprogramming; induced dopaminergic neuron.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electromagnetized MXenes Enhance the Efficient Direct Reprogramming of Dopamine Neurons for Parkinson's Disease Therapy.ACS Nano. 2025 May 6;19(17):16744-16759. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c01457. Epub 2025 Apr 21. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40257388
-
Functional integration of dopaminergic neurons directly converted from mouse fibroblasts.Cell Stem Cell. 2011 Nov 4;9(5):413-9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.09.011. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Cell Stem Cell. 2011. PMID: 22019014 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human spermatogonial stem cells to rescue parkinsonian phenotypes.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jun 27;10(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1294-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31248447 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Parkinson's Disease through the Use of Cell Reprogramming.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017 Apr;13(2):151-169. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9717-5. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017. PMID: 28083784 Review.
-
Cell reprogramming approaches in gene- and cell-based therapies for Parkinson's disease.J Control Release. 2018 Sep 28;286:114-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 17. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30026082 Review.
Cited by
-
Catalpol promotes the generation of cerebral organoids with oRGs through activation of STAT3 signaling.Bioeng Transl Med. 2024 Dec 29;10(3):e10746. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10746. eCollection 2025 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 40385540 Free PMC article.
-
PTN activity in quiescent neural stem cells mediates Shank3 overexpression-induced manic behavior.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 11;16(1):2435. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57699-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40069581 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease Modeling Using Directly Converted 3D Induced Dopaminergic Neuron Organoids and Assembloids.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(14):e2412548. doi: 10.1002/advs.202412548. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39965129 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
