Impact of ibrutinib on inflammation in a mouse model of Graves' orbitopathy
- PMID: 39280007
- PMCID: PMC11392736
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1420024
Impact of ibrutinib on inflammation in a mouse model of Graves' orbitopathy
Abstract
Introduction: Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) and interleukin (IL)-2 Inducible T-cell Kinase (ITK) inhibitors have anti-inflammatory properties. We investigated the therapeutic effect of ibrutinib, an orally bioavailable BTK/ITK inhibitor, in a mouse model of Graves' orbitopathy (GO).
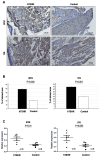
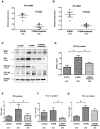
Methods: Genetic immunization was performed through intramuscular administration of the recombinant plasmid, pCMV6-hTSHR cDNA, to 8-week-old female BALB/c mice. Serum levels of T3, T4, and thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) antibodies (TRAbs) were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Histopathological changes in orbital tissues were examined using immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for TSHR and various inflammatory markers. Following successful genetic immunization, ibrutinib was orally administered daily for 2 weeks in the GO model mice. After treatment, the mRNA and protein expression levels of BTK, ITK, IL-1β, and IL-6 in orbital tissues were evaluated using real-time PCR and Western blotting.
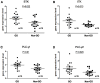
Results: In total, 20 mice were sacrificed to confirm successful genetic immunization. The GO mouse group exhibited significantly increased serum T3, T4, and TRAb levels. IHC revealed increased expression of TSHR, IL-1β, IL-6, transforming growth factor-β1, interferon-γ, CD40, CD4, BTK, and ITK in the GO mouse model. The orbital inflammation was significantly attenuated in ibrutinib-treated mice. The mRNA and protein expression levels of BTK, ITK, IL-1β, and IL-6 in orbital tissue were lower in ibrutinib-treated GO mouse group compared to the phosphate-buffered saline-treated GO mouse group.
Conclusion: The GO mouse model demonstrated enhanced BTK and ITK expression. Ibrutinib, a BTK/ITK inhibitor, suppressed the inflammatory cytokine production. These findings highlight the potential involvement of BTK/ITK in the inflammatory pathogenesis of GO, suggesting its role as a novel therapeutic target.
Keywords: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; Graves’ orbitopathy; ibrutinib; inflammation; interleukin-2 inducible T-cell kinase; mouse.
Copyright © 2024 Kim, Park, Choi, Jun, Chung, Park, Yoon, Yang and Jang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

