Magnetic stirring with iron oxide nanospinners accretes neurotoxic Aβ42 oligomers into phagocytic clearable plaques for Alzheimer's disease treatment
- PMID: 39280110
- PMCID: PMC11402446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101213
Magnetic stirring with iron oxide nanospinners accretes neurotoxic Aβ42 oligomers into phagocytic clearable plaques for Alzheimer's disease treatment
Abstract
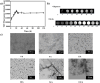
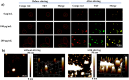
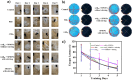
An increasing number of medications have been explored to treat the progressive and irreversible Alzheimer's disease (AD) that stands as the predominant form of dementia among neurodegenerative ailments. However, assertions about toxic side effects of these drugs are a significant hurdle to overcome, calling for drug-free nanotherapeutics. Herein, a new therapeutic strategy devoid of conventional drugs or other cytotoxic species was developed. The constructed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) nanospinners can accrete neurotoxic β-amyloid 42 oligomers (oAβ42) into aggregated magnetic plaques (mpAβ) by mechanical rotating force via remote interaction between nanoparticles and the applied magnetic field. While the cellular uptake of mpAβ attained from the magnetic stirring treatment by neuronal cells is severely limited, the facile phagocytic uptake of mpAβ by microglial cells leads to the polarization of the brain macrophages to M2 phenotype and thus the increased anti-inflammatory responses to the treatment. The SPION stirring treatment protects the AD mice from memory deterioration and maintain cognitive ability as evidenced from both nesting and Barnes maze tests. The examination of the oAβ42 injected brain tissues with the stirring treatment showed significant amelioration of functional impairment of neurons, microglia, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes alongside no obvious tissue damage caused by stirring meanwhile complete degradation of SPION was observed at day 7 after the treatment. The in vitro and animal data of this work strongly corroborate that this new modality of undruggable stirring treatment with SPIONs provides a new feasible strategy for developing novel AD treatments.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Microglial cell polarization; Nanoscaled stirring treatment; Phagocytic clearance; Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; β-Amyloid 42 oligomers.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors whose names are listed immediately below certify that they have declare no conflict of interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures






References
-
- Gustavsson A., Norton N., Fast T., Frölich L., Georges J., Holzapfel D., Kirabali T., Krolak-Salmon P., Rossini P.M., Ferretti M.T., Lanman L., Chadha A.S., van der Flier W.M. Global estimates on the number of persons across the Alzheimer's disease continuum. Alzheimer’s and dementia, Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023;19:658–670. - PubMed
-
- Madhu P., Mukhopadhyay S. Distinct types of amyloid-β oligomers displaying diverse neurotoxicity mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021;122:1594–1608. - PubMed
-
- Panza F., Lozupone M., Logroscino G., Imbimbo B.P. A critical appraisal of amyloid-β-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019;15:73–88. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

