Type of fixation is not associated with range of motion after operative treatment of proximal radius fractures- a systematic review of 519 patients
- PMID: 39280149
- PMCID: PMC11401575
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.04.011
Type of fixation is not associated with range of motion after operative treatment of proximal radius fractures- a systematic review of 519 patients
Abstract
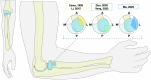
Background: The aims of this study are 1) to assess whether open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) techniques for fractures of the proximal radius are associated with the range of motion (ROM), 2) to determine the incidence of hardware-related complications and removal following plate and screw fixation of the proximal radius, and 3) to evaluate whether the safe-zone definition is described in the literature and its relation to the ROM.
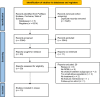
Methods: A literature search was performed in the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases. Studies reporting ROM in patients undergoing ORIF for radial head or neck fractures were included. Two treatment groups were defined based on ORIF technique: screws only or plates with and without additional screw placement.
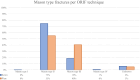
Results: A total of 13 articles were included with 519 patients, of which 271 belonged to the screw group and 248 to the plate group. At final follow-up, the screw group reported a mean supination of 79 (95% CI: 74-83), pronation of 76 (95% CI: 69-84), flexion of 131 (95% CI: 124-138), and loss of extension of 4 (95% CI: 1-7). The plate group reported a mean supination of 72 (95% CI: 65-80), pronation of 697 (95% CI: 60-75), flexion of 126 (95% CI: 118-133), and loss of extension of 7 (95% CI: 1-14).
Conclusion: Predominantly retrospective studies show that the ROM seems similar for screw and plate osteosynthesis of proximal radius fractures. Complication rates are similar as well. The safe-zone definition is rarely reported.
Keywords: Fracture fixation; ORIF; Postoperative complications; Proximal radius fractures; Range of motion; Revision surgery; Safe zone definition.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of a standard locking screw versus a double-threaded cortical compression screw for fixation of die-punch fragments in distal radius fractures with volar plating.Hand Surg Rehabil. 2020 Feb;39(1):30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.hansur.2019.10.195. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 31734295
-
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Demonstrates Better Outcomes Than Angular Stable Plate in the Treatment of Three-part and Four-part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Patients Older Than 70 Years.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Apr 1;481(4):735-747. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002480. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 36383078 Free PMC article.
-
Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures: ORIF with a volar fixed-angle tine plate versus external fixation.J Hand Surg Am. 2005 Mar;30(2):289-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2004.11.014. J Hand Surg Am. 2005. PMID: 15781351
-
Dorsal Bridge Plate for Distal Radius Fractures: A Systematic Review.J Hand Surg Am. 2021 Jul;46(7):627.e1-627.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2020.11.026. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Hand Surg Am. 2021. PMID: 33573844
-
The use of dorsal distraction plating for severely comminuted distal radius fractures: A review and comparison to volar plate fixation.Injury. 2019 Jun;50 Suppl 1:S50-S55. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2019.03.052. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Injury. 2019. PMID: 31040029 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
