Determining the efficacy of barbotage for pain relief in calcific tendinitis
- PMID: 39280166
- PMCID: PMC11401591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.06.005
Determining the efficacy of barbotage for pain relief in calcific tendinitis
Abstract
Background: Rotator cuff calcific tendinitis is a common cause of shoulder discomfort. Ultrasound-guided barbotage consists of needle aspiration and a subsequent lavage of calcium deposits in the shoulder. While barbotage has proven benefit, other options have also shown similar symptom improvement. This study aims to examine pain outcomes of patients following barbotage of calcific tendinitis. We hypothesize that barbotage will improve shoulder pain scores compared to preprocedure scores.
Methods: This is a retrospective chart review of 179 ultrasound-guided barbotage interventions for calcific tendinitis of the rotator at a New England urban medical center. Patient pain scores were analyzed using a Friedman's analysis of variance at a significance level of α = 0.05, and statistical significance between groups was elucidated using nonparametric post-hoc tests of significance between groups.
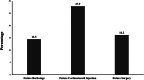
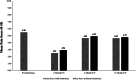
Results: Pain scores at preprocedure, 2-month, 6-month, and 12-month follow-ups yielded significant differences. Post-hoc nonparametric analysis revealed pain scores at 2 months were significantly lower than preprocedure and at 6 months. Additionally, 47.5% of cases in this study went on to require a secondary procedure of the respective shoulder after their barbotage treatment.
Conclusion: Upon analysis, utilization of barbotage as a treatment for calcific tendonitis of the shoulder appears to produce notable pain reduction in the short term (specifically at the 2-month follow-up), but begins to lose some efficacy over long-term evaluation. Additionally, a large portion of patients required further interventions of their shoulder, including corticosteroid injections, more barbotage, or surgery, raising further concerns over its long-term benefit.
Keywords: Aspiration and lavage; Barbotage; Calcific tendinitis; Corticosteroids; Pain management; Patient-reported outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Angileri H.S., Gohal C., Comeau-Gauthier M., Owen M.M., Shanmugaraj A., Terry M.A., et al. Chronic calcific tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing operative and nonoperative interventions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1746–1760. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.03.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arirachakaran A., Boonard M., Yamaphai S., Prommahachai A., Kesprayura S., Kongtharvonskul J. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy, ultrasound-guided percutaneous lavage, corticosteroid injection and combined treatment for the treatment of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy: a network meta-analysis of RCTs. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27:381–390. doi: 10.1007/s00590-016-1839-y. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
