Biologic augmentation of rotator cuff repair with microfragmented autologous subacromial bursal tissue enveloped in a patch of compressed autologous long head of biceps tendon tissue: the Bio-Ravioli technique
- PMID: 39280168
- PMCID: PMC11401564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.04.013
Biologic augmentation of rotator cuff repair with microfragmented autologous subacromial bursal tissue enveloped in a patch of compressed autologous long head of biceps tendon tissue: the Bio-Ravioli technique
Abstract
Background: Rotator cuff repair is one of the most frequently performed procedures in orthopedic surgery. However, considering the limited healing potential of rotator cuff tendons, several augmentation strategies have evolved to enhance tendon healing. The purpose of this article was to present a new surgical technique called Bio-Ravioli.
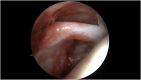
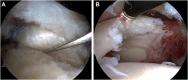
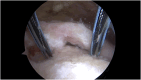
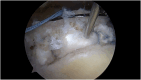
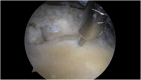
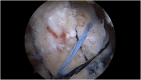
Methods: Patients with repairable full-thickness posterosuperior rotator cuff tear and a moderate-to-high risk of healing failure were chosen as candidates for the Bio-Ravioli procedure. It is a biologic augmentation strategy to increase healing potential of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair by use of a biologic graft fixed at the bone-tendon interface. The Bio-Ravioli consists of microfragmented autologous subacromial bursal tissue enveloped in a patch of compressed autologous long head of biceps tendon tissue. The rotator cuff is then repaired to the bone and over the graft using a transosseus equivalent configuration.
Conclusion: The Bio-Ravioli technique represents an easy and reliable way to increase the healing potential at the bone-tendon interface by using autologous mesenchymal stem cells from different sources: subacromial bursa and long head of the biceps tendon.
Keywords: Biologic enhancement; Long head of the biceps tendon; Mesenchymal stem cells; Rotator cuff repair; Subacromial bursa; Tendon healing.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
