Quality deterioration of mashed potatoes during the freeze-thaw cycle: From the perspective of moisture and microstructure
- PMID: 39280215
- PMCID: PMC11402148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101753
Quality deterioration of mashed potatoes during the freeze-thaw cycle: From the perspective of moisture and microstructure
Abstract
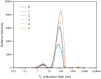
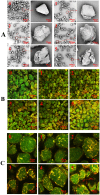
This study aimed to simulate cold chain sales temperatures to predict the effects of temperature fluctuations on the physicochemical properties, moisture distribution, microstructure, and flavor of mashed potatoes. The results showed a decline in the hardness and chewability of mashed potatoes alongside the migration of water from bound water states to weakly bound states under freeze-thaw cycles (FTC) conditions. Microstructural analysis indicated that the adhesive forces between proteins and starch granules were weakened, and the structure of mashed potatoes particles was destroyed following FTC. The oxidation and degradation of fat induced by FTC increased the content of key compounds such as octanal and nonanal, thereby contributing to an overall deterioration in the flavor of mashed potatoes. This study elucidates the effects of FTC on water migration, microstructure, and flavor characteristics of mashed potatoes, thereby providing a theoretical foundation for improving the quality of prefabricated frozen mashed potatoes dishes.
Keywords: Freeze-thaw cycles; Mashed potatoes; Microstructure; Volatile compounds; Water migration.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on the quality of Hot-dry noodles: From the moisture, starch, and protein characteristics.Food Chem. 2024 Jul 30;447:138996. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138996. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38492293
-
Rheological properties and microstructure of wheat flour dough systems with enzyme-hydrolyzed mashed potatoes.J Food Sci. 2024 Feb;89(2):941-953. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16916. Epub 2024 Feb 5. J Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38317415
-
Insights into the effect mechanism of freeze-thaw cycles on starch gel structure and quality characteristics of frozen extruded whole buckwheat noodles.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;278(Pt 1):134577. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134577. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39122075
-
Mashed potatoes enriched with soy protein isolate and inulin: chemical, rheological and structural basis.Food Sci Technol Int. 2013 Oct;19(5):447-60. doi: 10.1177/1082013212455347. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Food Sci Technol Int. 2013. PMID: 23733810
-
Effects of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on the Quality of a Novel Mixed Grain Composite Dough and Its Product (Potato-Oat Yu): Hybridization of Potatoes and Oats.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 11;9(16):18449-18457. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00294. eCollection 2024 Apr 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38680377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedi E., Sayadi M., Pourmohammadi K. Effect of freezing-thawing pre-treatment on enzymatic modification of corn and potato starch treated with activated α-amylase: Investigation of functional properties. Food Hydrocolloids. 2022;129
-
- Alvarez M.D., Fernández C., Canet W. Effect of cryoprotectant mixtures on rheological properties of fresh and frozen/thawed mashed potatoes. Journal of Food Process Engineering. 2011;34(2):224–250.
-
- Alvarez M.D., Fernández C., Solas M.T., Canet W. Viscoelasticity and microstructure of inulin-enriched mashed potatoes: Influence of freezing and cryoprotectants. Journal of Food Engineering. 2011;102(1):66–76.
-
- Chen Q.M., Xie Y.F., Yu H., Guo Y.H., Yao W.R. Non-destructive prediction of colour and water-related properties of frozen/thawed beef meat by Raman spectroscopy coupled multivariate calibration. Food Chemistry. 2023;413 - PubMed
-
- Cui M.L., Wang F.X., Li X.H., Yu J., Huang Y.Q., Liu Y.L. Investigation of the cryoprotective mechanisms of silver carp muscle hydrolysate for frozen dough exposed to multiple freeze-thaw cycles. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 2023;187:9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

