Single-cell multi-omics identify novel regulators required for osteoclastogenesis during aging
- PMID: 39280596
- PMCID: PMC11401210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110734
Single-cell multi-omics identify novel regulators required for osteoclastogenesis during aging
Abstract
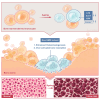
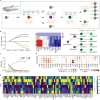
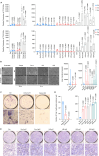
Age-related osteoporosis manifests as a complex pathology that disrupts bone homeostasis and elevates fracture risk, yet the mechanisms facilitating age-related shifts in bone marrow macrophages/osteoclasts (BMMs/OCs) lineage are not fully understood. To decipher these mechanisms, we conducted an investigation into the determinants controlling BMMs/OCs differentiation. We performed single-cell multi-omics profiling on bone marrow samples from mice of different ages (1, 6, and 20 months) to gain a holistic understanding of cellular changes across time. Our analysis revealed that aging significantly instigates OC differentiation. Importantly, we identified Cebpd as a vital gene for osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption during the aging process. Counterbalancing the effects of Cebpd, we found Irf8, Sox4, and Klf4 to play crucial roles. By thoroughly examining the cellular dynamics underpinning bone aging, our study unveils novel insights into the mechanisms of age-related osteoporosis and presents potential therapeutic targets for future exploration.
Keywords: Cell biology; Molecular biology; Omics; Transcriptomics.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Sui B., Hu C., Liao L., Chen Y., Zhang X., Fu X., Zheng C., Li M., Wu L., Zhao X., Jin Y. Mesenchymal progenitors in osteopenias of diverse pathologies: differential characteristics in the common shift from osteoblastogenesis to adipogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2016;6 doi: 10.1038/srep30186. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

