Plants' molecular behavior to heavy metals: from criticality to toxicity
- PMID: 39280950
- PMCID: PMC11392792
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1423625
Plants' molecular behavior to heavy metals: from criticality to toxicity
Abstract
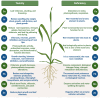
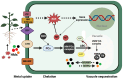
The contamination of soil and water with high levels of heavy metals (HMs) has emerged as a significant obstacle to agricultural productivity and overall crop quality. Certain HMs, although serving as essential micronutrients, are required in smaller quantities for plant growth. However, when present in higher concentrations, they become very toxic. Several studies have shown that to balance out the harmful effects of HMs, complex systems are needed at the molecular, physiological, biochemical, cellular, tissue, and whole plant levels. This could lead to more crops being grown. Our review focused on HMs' resources, occurrences, and agricultural implications. This review will also look at how plants react to HMs and how they affect seed performance as well as the benefits that HMs provide for plants. Furthermore, the review examines HMs' transport genes in plants and their molecular, biochemical, and metabolic responses to HMs. We have also examined the obstacles and potential for HMs in plants and their management strategies.
Keywords: agricultural productivity; cross-tolerance; genotoxicity; hormesis; molecular responses; transport genes.
Copyright © 2024 El-Sappah, Zhu, Huang, Chen, Soaud, Abd Elhamid, Yan, Li and El-Tarabily.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas M., Li Y., Elbaiomy R. G., Yan K., Ragauskas A. J., Yadav V., et al. . (2022). Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of SlHsp70 gene family in Solanum lycopersicum revealed higher expression of SlHsp70-11 in roots under Cd2+ stress. Front. Biosci. 27, 186. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2706186 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alam M. M., Hayat S., Ali B., Ahmad A. (2007). Effect of 28-homobrassinolide treatment on nickel toxicity in Brassica juncea . Photosynthetica 45, 139–142. doi: 10.1007/s11099-007-0022-4 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

