Oral probiotic administration attenuates postexercise inflammation in horses
- PMID: 39281311
- PMCID: PMC11401344
- DOI: 10.1093/tas/txae124
Oral probiotic administration attenuates postexercise inflammation in horses
Abstract
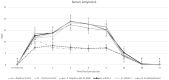
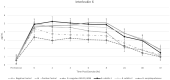
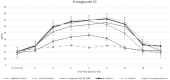
Probiotics are commonly incorporated into equine diets to impart health and performance benefits; however, peer-reviewed evidence supporting their efficacy in horses is limited. Interestingly, bacteria from the Bacillus genus are gaining interest for their unique ability to impact metabolic, immune, and inflammatory pathways. The objective of this trial was to evaluate a selection of Bacilli for their role in altering the inflammatory response in horses to exercise. Eighteen horses were utilized in a randomized cross-over trial. Horses were randomly assigned to one of 6 starting treatments including a negative and positive control, and groups that received one of 4 probiotics (Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086, Bacillus subtilis-1, Bacillus subtilis-2, or Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) top dressed to their daily ration at a rate of 8 billion CFU/d mixed into dried whey powder. All horses received a similar base diet of grass hay offered at 2.0% of bodyweight daily along with 4.54 kg of a commercially available textured horse feed. Each 3-wk phase of the trial consisted of a 2-wk dietary acclimation followed by a 1-wk exercise challenge and sample collection. Between phases, horses were offered only their base diet. On the day of exercise, horses were offered their 0700 ration and then subjected to a 2-h standardized exercise test. Blood samples were obtained prior to starting exercise and then again at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, 48, and 72-h postexercise. Horses in the positive control group were administered 0.23 mg/kg BW flunixin meglumine immediately following the 0-h sampling. Samples were analyzed for serum amyloid A (SAA), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) concentrations. Data were evaluated via ANOVA using the MIXED procedure in SAS 9.4. Exercise-induced inflammation as evidenced by SAA, IL-6, and PGE2 increases postexercise. Horses consuming B. coagulans GBI-30, 6086 had reduced production of SAA, IL-6, and PGE2 compared to all other probiotic-fed groups and the negative control (P < 0.001). The positive control successfully ameliorated the postexercise inflammatory response. These data highlight the potential for B. coagulans GBI-30, 6086 to be incorporated into equine rations as a method to support optimal response to exercise or other inflammation-inducing challenges. Additional research is ongoing to elucidate the methodology by which these results occur.
Keywords: equine; exercise; inflammation; nutrition; probiotic.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employed by Land O Lakes (Purina Animal Nutrition) at the time of this study. All appropriate declarations have been made.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary supplementation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product attenuates exercise-induced stress markers in young horses.J Anim Sci. 2021 Aug 1;99(8):skab199. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab199. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34181712 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on markers of joint inflammation and cartilage metabolism in young horses challenged with lipopolysaccharide.J Anim Sci. 2018 Mar 6;96(2):579-590. doi: 10.1093/jas/skx076. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 29385470 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of an oral joint supplement on gait kinematics and biomarkers of cartilage metabolism and inflammation in mature riding horses.Transl Anim Sci. 2020 Aug 24;4(3):txaa150. doi: 10.1093/tas/txaa150. eCollection 2020 Jul. Transl Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32968713 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 Improves Protein Absorption and Utilization.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018 Dec;10(4):611-615. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9354-y. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018. PMID: 29196920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
Cited by
-
Alternatives to antibiotics for sustainable livestock production in the context of the One Health approach: tackling a common foe.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Aug 13;12:1605215. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1605215. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40881639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ayala, D. I., Grum D. S., Evans N. P., Russo K. N., Kimminau E. A., Trible B. R., Lahoti M. M., Novak C. L., and Karnezos T. P... 2023. Identification and characterization of the causative agents of Focal Ulcerative Dermatitis in commercial laying hens. Front. Vet. Sci. 10:1110573. doi:10.3389/fvets.2023.1110573 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources