Small extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of response in recurrent/metastatic HNSCC patients treated with immunotherapy
- PMID: 39281316
- PMCID: PMC11390474
- DOI: 10.1038/s44276-024-00096-0
Small extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of response in recurrent/metastatic HNSCC patients treated with immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Biomarkers that effectively predict response to anti-PD-1 mAb therapy in cancer patients are an unmet need. We evaluated the utility of small extracellular vesicles (sEV) as biomarkers of response to immunotherapy in recurrent/metastatic (R/M) head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients.
Methods: Plasma sEV were isolated from 24 R/M HNSCC patients prior to immunotherapy initiation. sEV were separated by immune capture into T cell-derived CD3(+) and tumor-enriched CD3(-) subsets. Stimulatory and suppressive profiles of CD3(-) sEV were determined by on-bead flow cytometry. Differences were assessed using nonparametric tests. Multivariable Cox regression was used to evaluate the relationship with overall (OS) and progression free survival (PFS).
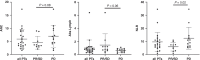
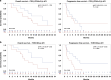
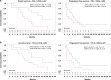
Results: CD3(-)CD44v3(+) sEV represented the majority of plasma sEV; the T-cell-derived CD3(+) fraction was significantly smaller. High CD3(+) sEV was associated with better OS and PFS. Total CD3(-)CD44v3(+) sEV was not associated with outcome. However, suppressive and stimulatory profiles were associated with OS; the suppressive/stimulatory ratio was associated with best response. Exploration of individual proteins on CD3(-) sEV showed that high PD-L1 and high CTLA-4 were associated with better outcomes.
Conclusions: Evaluation of the T cell-derived-CD3(+) and tumor-enriched CD3(-) plasma sEV subsets indicated their potential utility as biomarkers of response to immunotherapy.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsCompeting interests: None for C-SH, AS, RH, JA, BD and TLW. DPZ: Steering Committee (BICARA, Seagen Inc.); Consulting (Inhibrx, MacroGenics Inc.); Advisory Board (Merck, Prelude Therapeutics); Research support (institutional) for role as PI for clinical trials with Aduro Biotech Inc., Astra-Zeneca, Bicara Therapeutics Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, MacroGenics Inc., Merck, Novasenta. RLF: Adagene Incorporated: Consulting; Adaptimmune: H&N Cancer Advisory Board; Aduro Biotech, Inc: Consulting; Astra-Zeneca/MedImmune: Clinical Trial, Research Funding; Bicara Therapeutics, Inc: Consultant; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Advisory Board, Clinical Trial, Research Funding; Brooklyn Immunotherapeutics LLC: Consultant; Catenion: Consultant; Coherus BioSciences, Inc.: Advisory Board; CureVac : H&N Advisory Board; CytoAgents: Board; Eisai Europe Limited: Advisory Board; EMD Serono: Consultant; Everest Clinical Research Corporation: Consultant; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultant; Federation Bio, Inc: Consultant; Genocea Biosciences, Inc: Consultant; Genmab: Advisory Board; Hookipa Biotech GmbH: Advisory Board; Instil Bio, Inc: Advisory Board; Kowa Research Institute, Inc.: Consultant; Lifescience Dynamics Limited: Advisory Board; MacroGenics, Inc.: Advisory Board; MeiraGTx, LLC: Advisory Board; Merck: Advisory Board, Clinical Trial; Merus N.V: Advisory Board; Mirati Therapeutics, Inc: Consultant; Mirror Biologics Inc: Data Safety Monitoring Board; Nanobiotix: Consultant; Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Consulting; Novasenta: Consulting, Stock, Research Funding; Numab Therapeutics AG: Advisory Board; OncoCyte Corporation: Advisory Board; Pfizer: Advisory Board; PPD Development, L.P.: Consultant; Rakuten Medical, Inc: Advisory Board; Regeneron: H&N Advisory Board; Sanofi: Consultant; Seagen, Inc: Advisory Board; SIRPant Immunotherapeutics, Inc: Advisory Board; Tesaro: Research Funding; Vir Biotechnology, Inc: Advisory Board; Zymeworks, Inc.: Consultant.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024. 10.3322/caac.21820. - PubMed
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;394:1915–28. 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
