Interpretative structural modeling method: An analysis of influencing factors analysis on the adverse experiences of cardiac surgery patients in the intensive care units
- PMID: 39281500
- PMCID: PMC11402133
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36511
Interpretative structural modeling method: An analysis of influencing factors analysis on the adverse experiences of cardiac surgery patients in the intensive care units
Abstract
Objective: To construct an interpretation structure model of adverse experiences of cardiac surgery patients in intensive care unit, so as to provide a reference for optimizing the experience of critical patients step by step.
Methods: Literature review, semi-structured interviews, questionnaires and Delphi method were used to summarize and analyze the influencing factors of intensive care experience in cardiac surgery. The explanatory structural model was used to divide the influencing factors into levels and construct the explanatory structural model of adverse experience of cardiac surgery patients in intensive care.
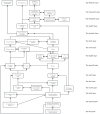
Results: A hierarchical structure model containing 34 elements and 15 levels was constructed, which were divided into Surface level, middle level and root level.
Conclusion: The intensive care experience of patients in cardiac surgery department is mainly affected by 34 factors. There are direct or indirect correlations between the influencing factors, and different levels have different effects.
Keywords: Bad experience; Cardiac surgery; Intensive care unit; Interpretative structural modeling method.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pain perception of patients in intensive care unit after cardiac surgery: A qualitative study using Roy's Adaptation Model.Nurs Crit Care. 2024 May;29(3):512-520. doi: 10.1111/nicc.12958. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Nurs Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 37527978
-
A comparison of the intensive care experiences of emergency and elective cardiac surgery patients.Niger J Clin Pract. 2016 Mar-Apr;19(2):284-9. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.175963. Niger J Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 26856296
-
The experiences of cardiac surgery critical care clinicians with in-bed cycling in adult patients undergoing complex cardiac surgery.Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Sep;44(18):5038-5045. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2021.1922515. Epub 2021 May 23. Disabil Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 34027750
-
Fast-track cardiac care for adult cardiac surgical patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Sep 12;9(9):CD003587. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003587.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27616189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Family members' perceptions of surrogate decision-making in the intensive care unit: A systematic review.Int J Nurs Stud. 2023 Jan;137:104391. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104391. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Int J Nurs Stud. 2023. PMID: 36442321
References
-
- Iosifyan M., Schmidt M., Hurbault A., et al. “I had the feeling that I was trapped”: a bedside qualitative study of cognitive and affective attitudes toward noninvasive ventilation in patients with acute respiratory failure. Ann. Intensive Care. 2019;9(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0608-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

