The effects of weather factors on road traffic casualties: Analysis on provincial panel data of China from 2006 to 2021
- PMID: 39281504
- PMCID: PMC11402167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36788
The effects of weather factors on road traffic casualties: Analysis on provincial panel data of China from 2006 to 2021
Abstract
Introduction: Road traffic injuries stands as a major concern globally, as they result in significant loss of life, economic impact, and erode trust in government and societal safety. The influence of weather on road traffic safety is undeniable, impacting road conditions, individuals, and vehicles. However, the specific influence of weather on road traffic casualties has seldom been explored.
Method: This study assesses the effect of weather factors on road traffic casualties in China from 2006 to 2021. Vector error correction models (VECM) were utilized to determine the Granger causality between weather factors and covariates. Furthermore, panel autoregressive distribution lag models (ARDL) were applied to quantify the association between weather factors and road traffic casualties.
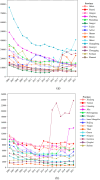
Results: The findings indicate that rainfall and temperature exert a short-term negative impact on casualty risk, which intriguingly becomes positive in the long term. A standout discovery is the significant role of health investments, which are shown to reduce casualty numbers in both the short and long-terms. In the long run, the gross domestic product significantly enhances casualties, while expressway mileage notably decreases them.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate the significant influence of weather on road traffic casualties and highlight the critical roles played by factors such as gross domestic product, health investment, and expressway mileage. The evidence presented in the study underscores the urgent need for more effective strategies to mitigate road traffic casualties. Thus, some effective measures are proposed to reduce road traffic casualties. This study is conducive to the improvement of traffic in severe weather in China and provides guidance for traffic management departments.
Keywords: ARDL model; Rainfall; Road traffic safety; Temperature.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Road traffic safety: An analysis of the cross-effects of economic, road and population factors.Chin J Traumatol. 2019 Oct;22(5):290-295. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.07.004. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Chin J Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 31506232 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of temperature, rainfall, and health worker density index on road traffic fatalities in Pakistan.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jun;27(16):19510-19529. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08233-1. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32215794
-
General dependencies and causality analysis of road traffic fatalities in OECD countries.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jul;25(20):19612-19627. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2146-4. Epub 2018 May 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29736640
-
Characteristics, likelihood and challenges of road traffic injuries in China before COVID-19 and in the postpandemic era.Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2023;10(1):2. doi: 10.1057/s41599-022-01482-0. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2023. PMID: 36619597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traffic accidents involving fatigue driving and their extent of casualties.Accid Anal Prev. 2016 Feb;87:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2015.10.033. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Accid Anal Prev. 2016. PMID: 26625173 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Road traffic injuries—fact sheet. 2018. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs358/en/ from.
-
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zgtjnj/
-
- Wang R., Gong J., Wang Y., Chen H., Chen S., Wang Q. Relationship between gross domestic product and accident in China. J. Saf. Studies. 2017;3:19–26.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

