Increased circulating LOX-1+ neutrophils activate T cells and demonstrate a pro-inflammatory role in allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 39281616
- PMCID: PMC11398634
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36218
Increased circulating LOX-1+ neutrophils activate T cells and demonstrate a pro-inflammatory role in allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Low-density neutrophils are heterogeneous immune cells with immunosuppressive (such as polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells [PMN-MDSC]) or pro-inflammatory (such as low-density granulocytes [LDG]) properties that have been well described in multiple cancers and immune diseases. However, its role in allergic rhinitis (AR) is still unclear.
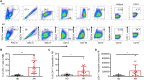
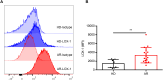
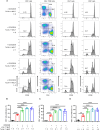
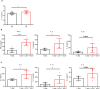
Methods: In the present study, we defined low-density neutrophils as CD14-CD11B+CD15+LOX-1+ (LOX-1+ neutrophils), and their levels in the peripheral blood (PB) were evaluated and compared between patients with AR and healthy donors using flow cytometric analysis. LOX-1 expression on polymorphonuclear neutrophils was identified. Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-stained CD3+ T cells were cultured alone or with LOX-1+ neutrophils, T cell proliferation was assessed using flow cytometry, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the supernatants were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clinicopathological analyses were performed to gain a thorough understanding of LOX-1+ neutrophils.
Results: We determined that LOX-1+ neutrophils were significantly increased in the PB of patients with AR, and LOX-1 expression in neutrophils from patients with AR was elevated. Interestingly, LOX-1+ neutrophils derived from patients with AR, unlike PMN-MDSC, promoted T cell proliferation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Moreover, clinicopathological analysis revealed that there was no any relation between circulating LOX-1+ neutrophil levels and the levels of IgE, age and sex.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that elevated circulating LOX-1+ neutrophils play a pro-inflammatory role in AR.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; LOX-1+ neutrophils; Low-density neutrophils; Pro-inflammatory role.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Bousquet J., Anto J.M., Bachert C., Baiardini I., Bosnic-Anticevich S., Canonica G.W., Melen E., Palomares O., Scadding G.K., Togias A., et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020;6(1):95. - PubMed
-
- Wang X.D., Du K., She W.Y., Ouyang Y.H., Sima Y.T., Liu C.Y., Zhang L. Recent advances in the diagnosis of allergic rhinitis. Expet Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018;14(11):957–964. - PubMed
-
- Devillier P., Bousquet J., Salvator H., Naline E., Grassin-Delyle S., de Beaumont O. In allergic rhinitis, work, classroom and activity impairments are weakly related to other outcome measures. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2016;46(11):1456–1464. - PubMed
-
- Wise S.K., Damask C., Roland L.T., Ebert C., Levy J.M., Lin S.D., Luong A., Rodriguez K., Sedaghat A.R., Toskala E., et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: allergic rhinitis-2023. Int Forum Allergy Rh. 2023;13(4):293–859. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Pino M.D., Richardson W.S., Zabaleta J., Puttalingaiah R.T., Chapple A.G., Liu J., Kim Y., Ponder M., DeArmitt R., Baiamonte L.B., et al. Increased inflammatory low-density neutrophils in severe obesity and effect of bariatric surgery: results from case-control and prospective cohort studies. EBioMedicine. 2022;77:103910. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

