Advancements in nuclear imaging using radiolabeled nanobody tracers to support cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 39281708
- PMCID: PMC11402390
- DOI: 10.1093/immadv/ltae006
Advancements in nuclear imaging using radiolabeled nanobody tracers to support cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
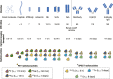
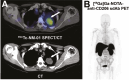
The evolving landscape of cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment. However, the dynamic tumor microenvironment has led to variable clinical outcomes, indicating a need for predictive biomarkers. Noninvasive nuclear imaging, using radiolabeled modalities, has aided in patient selection and monitoring of their treatment response. This approach holds promise for improving diagnostic accuracy, providing a more personalized treatment regimen, and enhancing the clinical response. Nanobodies or single-domain antibodies, derived from camelid heavy-chain antibodies, allow early timepoint detection of targets with high target-to-background ratios. To date, a plethora of nanobodies have been developed for nuclear imaging of tumor-specific antigens, immune checkpoints, and immune cells, both at a preclinical and clinical level. This review comprehensively outlines the recent advancements in nanobody-based nuclear imaging, both on preclinical and clinical levels. Additionally, the impact and expected future advancements on the use of nanobody-based radiopharmaceuticals in supporting cancer diagnosis and treatment follow-up are discussed.
Keywords: cancer; diagnostics; immunotherapy; nanobodies; nuclear imaging.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Nick Devoogdt is co-founder of the companies Precirix and Abscint.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
