Sustainability and cost of typical and heart-healthy dietary patterns in Australia
- PMID: 39282012
- PMCID: PMC11399559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2024.100448
Sustainability and cost of typical and heart-healthy dietary patterns in Australia
Abstract
Study objective: The aim was to quantify and compare the environmental and financial impact of two diets: a heart-healthy Australian diet (HAD) and the typical Australian diet (TAD).
Design: The study involved a secondary analysis of two modelled dietary patterns used in a cross-over feeding trial.
Setting: The evaluation focused on two-week (7-day cyclic) meal plans designed to meet the nutritional requirements for a reference 71-year-old male (9000 kJ) for each dietary pattern.
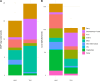
Main outcome measures: The environmental footprint of each dietary pattern was calculated using the Global Warming Potential (GWP*) metric, taking into account single foods, multi-ingredient foods, and mixed dishes. Prices were obtained from a large Australian supermarket.
Results: The HAD produced 23.8 % less CO2 equivalents (CO2e) per day (2.16 kg CO2e) compared to the TAD (2.83 kg CO2e per day). Meat and discretionary foods were the primary contributors to the environmental footprint of the TAD, whereas dairy and vegetables constituted the largest contributors to the HAD footprint. However, the HAD was 51 % more expensive than the TAD.
Conclusion: Transitioning from a TAD to a HAD could significantly reduce CO2 emissions and with benefits for human health and the environment. Affordability will be a major barrier. Strategies to reduce costs of convenient healthy food are needed. Future studies should expand the GWP* database and consider additional environmental dimensions to comprehensively assess the impact of dietary patterns. Current findings have implications for menu planning within feeding trials and for individuals seeking to reduce their carbon footprint while adhering to heart-healthy eating guidelines.
Keywords: Carbon footprint; Climate change; Dietary patterns; Global warming.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest with regard to the research, authorship and publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Swinburn B.A., Kraak V.I., Allender S., Atkins V.J., Baker P.I., Bogard J.R., et al. The global syndemic of obesity, undernutrition, and climate change: the lancet commission report. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):791–846. - PubMed
-
- Pörtner H.-O., Roberts D., Tignor M., Poloczanska E., Mintenbeck K., Alegría A., et al. 2022. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability Working Group II Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
-
- Rosenzweig C., Mbow C., Barioni L.G., Benton T.G., Herrero M., Krishnapillai M., et al. Climate change responses benefit from a global food system approach. Nat. Food. 2020;1(2):94–97. - PubMed
-
- UN Secretary-general's chair summary and statement of action on the UN Food Systems Summit. 2021. https://www.un.org/en/food-systems-summit/news/making-food-systems-work-... Available from:
-
- Ranganathan J., Waite R., Searchinger T., Hanson C. 2018. How to Sustainably Feed 10 Billion People by 2050, in 21 Charts.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

