Developing a calculable risk prediction model for sternal wound infection after median sternotomy: a retrospective study
- PMID: 39282020
- PMCID: PMC11401447
- DOI: 10.1093/burnst/tkae031
Developing a calculable risk prediction model for sternal wound infection after median sternotomy: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Diagnosing sternal wound infection (SWI) following median sternotomy remains laborious and troublesome, resulting in high mortality rates and great harm to patients. Early intervention and prevention are critical and challenging. This study aimed to develop a simple risk prediction model to identify high-risk populations of SWI and to guide examination programs and intervention strategies.
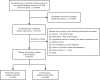
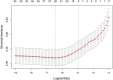
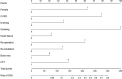
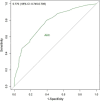
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data obtained from 6715 patients who underwent median sternotomy between January 2016 and December 2020. The least absolute shrink and selection operator (LASSO) regression method selected the optimal subset of predictors, and multivariate logistic regression helped screen the significant factors. The nomogram model was built based on all significant factors. Area under the curve (AUC), calibration curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to assess the model's performance.
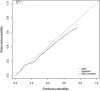
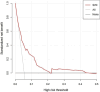
Results: LASSO regression analysis selected an optimal subset containing nine predictors that were all statistically significant in multivariate logistic regression analysis. Independent risk factors of SWI included female [odds ratio (OR) = 3.405, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 2.535-4.573], chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (OR = 4.679, 95% CI = 2.916-7.508), drinking (OR = 2.025, 95% CI = 1.437-2.855), smoking (OR = 7.059, 95% CI = 5.034-9.898), re-operation (OR = 3.235, 95% CI = 1.087-9.623), heart failure (OR = 1.555, 95% CI = 1.200-2.016) and repeated endotracheal intubation (OR = 1.975, 95% CI = 1.405-2.774). Protective factors included bone wax (OR = 0.674, 95% CI = 0.538-0.843) and chest physiotherapy (OR = 0.446, 95% CI = 0.248-0.802). The AUC of the nomogram was 0.770 (95% CI = 0.745-0.795) with relatively good sensitivity (0.798) and accuracy (0.620), exhibiting moderately good discernment. The model also showed an excellent fitting degree on the calibration curve. Finally, the DCA presented a remarkable net benefit.
Conclusions: A visual and convenient nomogram-based risk calculator built on disease-associated predictors might help clinicians with the early identification of high-risk patients of SWI and timely intervention.
Keywords: Median sternotomy; Nomogram; Postcardiac surgical complications; Prediction model; Sternal wound infection.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk factors for sternal wound infection after median sternotomy: A nested case-control study and time-to-event analysis.Int Wound J. 2024 Jul;21(7):e14965. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14965. Int Wound J. 2024. PMID: 38994878 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors of infected sternal wounds versus sterile wound dehiscence.J Surg Res. 2016 Jan;200(1):400-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.07.045. Epub 2015 Aug 7. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 26371410
-
Developing a prediction model for preoperative acute heart failure in elderly hip fracture patients: a retrospective analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Sep 14;25(1):736. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07843-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39277727 Free PMC article.
-
A Nomogram to Predict the Risk of Acute Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2024;14(1):46-57. doi: 10.1159/000539015. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2024. PMID: 38648746 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of 28 day-mortality risk factors in sepsis patients and construction and validation of predictive model].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 May;36(5):478-484. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231109-00961. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38845493 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Precision prediction of intervertebral disc degeneration in ankylosing spondylitis using a nomogram model reveals the pivotal role of Th2-type immune dysregulation.Front Immunol. 2025 May 12;16:1556738. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1556738. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40421015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lemaignen A, Birgand G, Ghodhbane W, Alkhoder S, Lolom I, Belorgey S, et al. . Sternal wound infection after cardiac surgery: incidence and risk factors according to clinical presentation. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015;21:674.e11–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

