Effect of body size on the oral pharmacokinetics of oxytetracycline in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
- PMID: 39282114
- PMCID: PMC11401510
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17973
Effect of body size on the oral pharmacokinetics of oxytetracycline in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the plasma pharmacokinetics of oxytetracycline (OTC) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) of different body sizes.
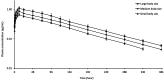
Methods: The research was carried out on three groups as small (30-50 g), medium (90-110 g) and large (185-215 g) body sizes at 8 ± 0.5 °C. OTC was administered orally at a dose of 60 mg/kg to all groups. Blood samples were taken at 19 different sampling times until the 384 h after oxytetracycline administration. The plasma concentrations of OTC were measured using high pressure liquid chromatography-ultraviolet and pharmacokinetic parameters were evaluated using non-compartmental analysis.
Results: OTC was detected in small-body sized fish until the 336 h and in medium and large-body sized fish until the 384 h. The elimination half-life of OTC was 85.46, 87.24 and 86.98 h in the small, medium and large body size groups, respectively. The peak plasma concentration increased from 0.66 to 1.11 µg/mL, and the area under the plasma concentration-versus time curve from zero (0) h to infinity (∞) increased from 87.86 to 151.52 h*µg/mL, in tandem with the increase in fish body size. As fish body size increased, volume of distribution and total body clearance decreased.
Conclusion: These results show that the pharmacokinetics of OTC vary depending on fish size. Therefore, there is a need to reveal the pharmacodynamic activity of OTC in rainbow trout of different body sizes.
Keywords: Body size; HPLC; Oxytetracycline; Pharmacokinetics; Rainbow trout.
©2024 Corum et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Önder Yıldırım is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures
References
-
- Abedini S, Namdari R, Law FCP. Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of oxytetracycline in rainbow trout and chinook salmon. Aquaculture. 1998;162:23–32. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(97)00306-2. - DOI
-
- Amit R, Sahu NP, Subodh G, Aklakur M. Prospects of medicated feed in aquaculture. Nutrition and Food Science International Journal. 2017;3:555617.
-
- Björklund H, Bylund G. Temperature-related absorption and excretion of oxytetracycline in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.) Aquaculture. 1990;84:363–372. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(90)90101-R. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials