Immunomodulation and Humoral Immune Response in Teleost Immunized with Aeromonas-Derived Antigenic Extracellular Bioactive Molecules
- PMID: 39282170
- PMCID: PMC11399544
- DOI: 10.1007/s12088-024-01254-1
Immunomodulation and Humoral Immune Response in Teleost Immunized with Aeromonas-Derived Antigenic Extracellular Bioactive Molecules
Abstract
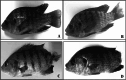
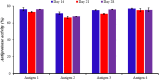
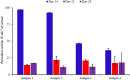
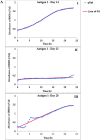
The common use of antimicrobials in food-animal production can lead to drug residues in edible tissues for consumers. However, immunomodulators enhance immune responses and vaccine effectiveness. A new perspective explores bacterial extracellular bioactive molecules (EBMs) in food-animal production to modulate host immune responses, potentially transforming pathogen management and antimicrobial use. This study investigates the immunogenic potential of Aeromonas hydrophila-derived EBMs (Antigens) to enhance the immune system. Four Antigens were administered intraperitoneally to Oreochromis niloticus (Nile Tilapia). Antigens 2 and Antigens 3 boosted fish immune competence within 21 days. Remarkably, Antigens 3 induced robust immunity against A. hydrophila with a single dose, notably enhancing antibody-based immune responses. The increased antibody activity suggests Antigens 3 could be a vaccine candidate, promising further research and potential application in food-animal production to improve disease control. This study highlights immunomodulators' potential in reshaping disease management in the food-animal industry, emphasizing the benefits of focusing on bacterial EBMs to reduce reliance on antimicrobials and achieve sustainable disease prevention.
Keywords: Aeromonas; Antigen; Antimicrobial resistance (AMR); Extracellular bioactive molecules (EBMs); Humoral Immunity; Immunization; Immunomodulation.
© Association of Microbiologists of India 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declared that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2020) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
-
- Rocha CP, Cabral HN, Marques JC, Goncalves AM (2022) A global overview of Aquaculture Food production with a focus on the activity’s development in transitional systems—the case study of a South European country (Portugal). J Mar Sci Eng 10:417. 10.3390/jmse10030417 10.3390/jmse10030417 - DOI
-
- Olga H (2017) Major bacterial diseases affecting aquaculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Aquatic AMR Workshop, vol 1, pp 10–11
-
- Dar GH, Kamili AN, Chishti MZ, Dar SA, Tantry TA, Ahmad F (2016) Characterization of Aeromonas sobria isolated from fish Rohu (Labeo rohita) collected from polluted pond. J Bacteriol Parasitol. 10.4172/2155-9597.1000273 10.4172/2155-9597.1000273 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
