Using in silico methods to determine optimal tapering regimens for decanoate-based long-acting injectable psychosis drugs
- PMID: 39282238
- PMCID: PMC11401015
- DOI: 10.1177/20451253241272790
Using in silico methods to determine optimal tapering regimens for decanoate-based long-acting injectable psychosis drugs
Abstract
Background: Reducing the dose of psychosis drugs in a gradual hyperbolic manner may minimise withdrawal effects and risk of relapse. There is presently limited guidance on tapering decanoate-based long-acting injectable dopamine antagonists (LIDAs).
Objectives: We aimed to apply hyperbolic principles of tapering to the decanoate-based LIDAs flupentixol, zuclopenthixol and haloperidol to develop withdrawal regimens.
Design: We used in silico methodology to predict plasma drug levels and D2 occupancy for different LIDA regimens.
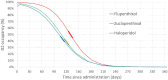
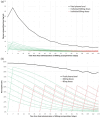
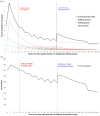
Methods: Existing pharmacokinetic and receptor occupancy data from nuclear neuroimaging studies were used to power modelling. Abrupt discontinuation was examined as a potential strategy, and dose reduction was modelled with pre-defined constraints used in similar work of 10 (fast regimens), 5 (moderate) and 2.5 (slow) percentage points of D2 occupancy change per month.
Results: Abrupt discontinuation of decanoate-based LIDAs leads to excessive change in D2 occupancy which violated our pre-defined constraints, potentially resulting in withdrawal symptoms and increased risk of relapse. Reduction of LIDA dose allowed hyperbolic reduction in plasma level consistent with imposed constraints on receptor occupancy reduction rate. For equivalent per-weekly LIDA dosing, more frequent administration allowed a more gradual reduction of D2 occupancy. However, switching to oral forms is required to continue hyperbolic tapering to full discontinuation; reduction to zero using only LIDA produces too large a reduction in D2 occupancy. Guidance for reduction and cessation of LIDAs according to slow, moderate and fast criteria is provided.
Conclusion: Abrupt cessation of decanoate LIDAs is not consistent with gradual hyperbolic tapering, despite their longer half-lives compared with oral formulations. Reduction to the point of full discontinuation can only be achieved by switching to oral therapy to complete the taper. These results are limited by the in silico and theoretical nature of the study, and there is a need to confirm these findings through real-world observational and interventional studies.
Keywords: antipsychotic; depot; discontinuation; flupentixol; haloperidol; hyperbolic; reduction; withdrawal; zuclopenthixol.
Plain language summary
Computer-based research on the best way to reduce the dose and eventually stop three depot antipsychotics What is the problem? Psychosis affects how someone experiences reality. Antipsychotics are used to treat psychosis. They work by blocking a chemical called dopamine. Stopping these too rapidly can cause psychosis to occur again. This might be because the dopamine block is removed suddenly. Sometimes antipsychotics are given by injection. Injections stay in the body for a longer time than tablets. The best way to reduce these injections is currently unknown. What did we do? We explored the best way to reduce and stop antipsychotic injections. We looked at three different types of psychosis injection. We used existing data to assess how these drugs affect the brain. We examined what would happen if an antipsychotic injection was suddenly stopped. We then evaluated the effect of reducing the dose gradually. What did we find? Stopping antipsychotic injections suddenly would lead to rapid changes at brain receptors. This might lead to symptoms of withdrawal and a high risk of psychosis recurring. Reducing the dose of injections leads to less change than stopping suddenly. Switching to a tablet allows for more control when reducing dose. Having injections more often also reduce the changes occurring between injections. We outline three different rates of dose reduction. What does this mean? Antipsychotic injections stay in the body longer than tablets. However, stopping injections suddenly may still not be safe. We recommend that people reduce the dose of their injection instead. We also recommend people switch to tablets or liquid before stopping. It should be noted that our research is computer-based. We would like to see our recommendations tested in the real world.
© The Author(s), 2024.
Figures
References
-
- OpenPrescribing. Antipsychotic depot injections, https://openprescribing.net/bnf/040202/ (2023, accessed 13 November 2023).
-
- NHS Business Services Authority. Prescription cost analysis – England 2021/22, https://nhsbsa-opendata.s3.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/pca/pca_summary_table... (2022, accessed 26 September 2022).
-
- Moncrieff J, Crellin N, Stansfield J, et al. Antipsychotic dose reduction and discontinuation versus maintenance treatment in people with schizophrenia and other recurrent psychotic disorders in England (the RADAR trial): an open, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Psychiatry 2023; 10(11): P848–P859. - PubMed
-
- Wunderink L, Nieboer RM, Wiersma D, et al. Recovery in remitted first-episode psychosis at 7 years of follow-up of early dose reduction/discontinuation or maintenance treatment strategy. JAMA Psychiatry 2013; 70: 913–920. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

