This is a preprint.
HLA-E and NKG2A Mediate Resistance to BCG Immunotherapy in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 39282294
- PMCID: PMC11398371
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.02.610816
HLA-E and NKG2A Mediate Resistance to BCG Immunotherapy in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Abstract
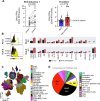
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is the first-line therapy for high-grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), yet many patients experience recurrence due to immune evasion. We identify HLA-E and NKG2A as mediators of adaptive resistance involving chronic activation of NK and T cells in BCG-unresponsive tumors. Prolonged IFN-γ exposure enhances HLA-E and PD-L1 expression on recurrent tumors, accompanied by the accumulation of NKG2A+ NK and CD8 T cells. HLA-Ehigh tumor cells preferentially cluster near CXCL12-rich stromal regions with dense effector cell presence, underscoring a spatially segregated tumor architecture. Although cytotoxic lymphocytes retain effector potential, their activity is restrained by HLA-E/NKG2A and PD-L1/PD-1 pathways located in their immediate neighborhood within the bladder tumor microenvironment. These data reveal a spatially organized immune escape program that limits anti-tumor immunity. Our findings support dually targeting NKG2A and PD-L1 checkpoint blockade as a rational, bladder-sparing strategy for patients with BCG-unresponsive NMIBC.
Keywords: BCG-unresponsive; Immunotherapy; NK cells; Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest. DECLARATION OF INTERESTS A.H. receives research funds from Astra Zeneca and has recently served on the advisory boards of Immunorizon, Purple Biotech, enGene, and Moexa Pharmaceuticals. N.B. is an extramural member of the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, receives research funds from Regeneron, Harbor Biomedical, DC Prime, and Dragonfly Therapeutics and is on the advisory boards of Neon Therapeutics, Novartis, Avidea, Boehringer Ingelheim, Rome Therapeutics, Rubius Therapeutics, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, BreakBio, Carisma Therapeutics, CureVac, Genotwin, BioNTech, Gilead Therapeutics, Tempest Therapeutics, and the Cancer Research Institute. LD has sponsored research agreements with C2i Genomics, Veracyte, Natera, AstraZeneca, Photocure, and Ferring and serves in an advisory/consulting role for Ferring, MSD, Cystotech, and UroGen. LD has received speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Roche.
Figures





References
-
- Ranti D., Bieber C., Wang Y.S., Sfakianos J.P., and Horowitz A. (2022). Natural killer cells: unlocking new treatments for bladder cancer. Trends Cancer. 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.03.007. - DOI
-
- Kamat A.M., Li R., O’Donnell M.A., Black P.C., Roupret M., Catto J.W., Comperat E., Ingersoll M.A., Witjes W.P., McConkey D.J., and Witjes J.A. (2018). Predicting Response to Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Immunotherapy: Are We There Yet? A Systematic Review. Eur Urol 73, 738–748. 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.10.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li R., Hensley P.J., Gupta S., Al-Ahmadie H., Babjuk M., Black P.C., Brausi M., Bree K.K., Fernandez M.I., Guo C.C., et al. (2024). Bladder-sparing Therapy for Bacillus Calmette-Guerin-unresponsive Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: International Bladder Cancer Group Recommendations for Optimal Sequencing and Patient Selection. Eur Urol 86, 516–527. 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.08.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 CA244780/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI168632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA264032/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA274148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI187598/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA269954/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI130760/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS111997/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA301050/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271545/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R61 CA278402/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 CA297580/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD032720/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS127984/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA058527/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM142918/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA196521/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
