This is a preprint.
Structure and inhibition mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis essential transporter efflux protein A
- PMID: 39282303
- PMCID: PMC11398473
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.04.611325
Structure and inhibition mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis essential transporter efflux protein A
Update in
-
Structure and inhibition mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis essential transporter efflux protein A.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 1;16(1):3139. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58133-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40169593 Free PMC article.
Abstract
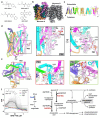
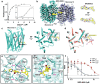
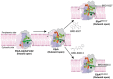
A broad chemical genetics screen in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) to identify inhibitors of established or previously untapped targets for therapeutic development yielded compounds (BRD-8000.3 and BRD-9327) that inhibit the essential efflux pump EfpA. To understand the mechanisms of inhibition by these compounds, we determined the structures of EfpA with inhibitors bound at 2.7 - 3.4 Å resolution. Our structures reveal different mechanisms of inhibition for the two inhibitors. BRD-8000.3 binds in a tunnel making contact with the lipid bilayer and extending toward the central cavity to displace the fatty acid chain of a lipid molecule bound in the apo structure, suggesting its blocking of an access route for a natural lipidic substrate, in contrast to its uncompetitive mechanism for the small molecule substrate ethidium bromide which likely enters through an alternative tunnel. Meanwhile, BRD-9327 binds in the outer vestibule without complete blockade of the substrate path to the outside, suggesting its possible inhibition of the dynamical motion necessary for "alternate access" to the two different sides of the membrane, as is characteristic of major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporters. Both inhibitors may have a role in inhibiting the "alternate access" mechanism that could account for the uncompetitive nature of their efflux of some substrates. Our results explain the basis of the synergy of these inhibitors and their potential for combination in a multi drug strategy for anti-tuberculosis therapy. They also potentially point to a possible function for this essential efflux pump as a lipid transporter. The structures provide a foundation for rational modification of these inhibitors to increase potency.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: N.K.K., M.G., S.B., J.E.G., Z.G., A.Y.E., S.G.B., A.S., D.T.H. and R.M.S. declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Organization, W.H. Tuberculosis Global Health Report November 2023. (2023).
-
- Johnson E.O. et al. Large-scale chemical-genetics yields new M. tuberculosis inhibitor classes. Nature 571, 72–78 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
