This is a preprint.
Claudin-4 remodeling of nucleus-cell cycle crosstalk maintains ovarian tumor genome stability and drives resistance to genomic instability-inducing agents
- PMID: 39282307
- PMCID: PMC11398366
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.04.611120
Claudin-4 remodeling of nucleus-cell cycle crosstalk maintains ovarian tumor genome stability and drives resistance to genomic instability-inducing agents
Abstract
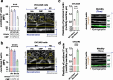
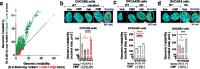
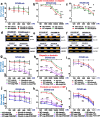
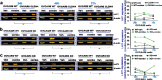
During cancer development, the interplay between the nucleus and the cell cycle leads to a state of genomic instability, often accompanied by observable morphological aberrations. These aberrations can be controlled by tumor cells to evade cell death, either by preventing or eliminating genomic instability. In epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), overexpression of the multifunctional protein claudin-4 is a key contributor to therapy resistance through mechanisms associated with genomic instability. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying claudin-4 overexpression in EOC remain poorly understood. Here, we altered claudin-4 expression and employed a unique claudin-4 targeting peptide (CMP) to manipulate the function of claudin-4. We found that claudin-4 facilitates genome maintenance by linking the nuclear envelope and cytoskeleton dynamics with cell cycle progression. Claudin-4 caused nuclei constriction by excluding lamin B1 and promoting perinuclear F-actin accumulation, associated with remodeling nuclear architecture, thus altering nuclear envelope dynamics. Consequently, cell cycle modifications due to claudin-4 overexpression resulted in fewer cells entering the S-phase and reduced genomic instability. Importantly, disrupting biological interactions of claudin-4 using CMP and forskolin altered oxidative stress cellular response and increased the efficacy of PARP inhibitor treatment. Our data indicate that claudin-4 protects tumor genome integrity by remodeling the crosstalk between the nuclei and the cell cycle, leading to resistance to genomic instability formation and the effects of genomic instability-inducing agents.
Keywords: HIF-1; LAT1; Ovarian cancer; PARPi; ROS; forskolin; genomic integrity; lamin B1; nuclei; perinuclear F-actin.
Figures


References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov 2022;12(1):31–46 doi 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
