This is a preprint.
A next-generation, histological atlas of the human brain and its application to automated brain MRI segmentation
- PMID: 39282320
- PMCID: PMC11398399
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.05.579016
A next-generation, histological atlas of the human brain and its application to automated brain MRI segmentation
Update in
-
A probabilistic histological atlas of the human brain for MRI segmentation.Nature. 2025 Dec;648(8094):678-685. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09708-2. Epub 2025 Nov 5. Nature. 2025. PMID: 41193801 Free PMC article.
Abstract
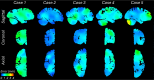
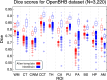
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the standard tool to image the human brain in vivo. In this domain, digital brain atlases are essential for subject-specific segmentation of anatomical regions of interest (ROIs) and spatial comparison of neuroanatomy from different subjects in a common coordinate frame. High-resolution, digital atlases derived from histology (e.g., Allen atlas [7], BigBrain [13], Julich [15]), are currently the state of the art and provide exquisite 3D cytoarchitectural maps, but lack probabilistic labels throughout the whole brain. Here we present NextBrain, a next-generation probabilistic atlas of human brain anatomy built from serial 3D histology and corresponding highly granular delineations of five whole brain hemispheres. We developed AI techniques to align and reconstruct ~10,000 histological sections into coherent 3D volumes with joint geometric constraints (no overlap or gaps between sections), as well as to semi-automatically trace the boundaries of 333 distinct anatomical ROIs on all these sections. Comprehensive delineation on multiple cases enabled us to build the first probabilistic histological atlas of the whole human brain. Further, we created a companion Bayesian tool for automated segmentation of the 333 ROIs in any in vivo or ex vivo brain MRI scan using the NextBrain atlas. We showcase two applications of the atlas: automated segmentation of ultra-high-resolution ex vivo MRI and volumetric analysis of Alzheimer's disease and healthy brain ageing based on ~4,000 publicly available in vivo MRI scans. We publicly release: the raw and aligned data (including an online visualisation tool); the probabilistic atlas; the segmentation tool; and ground truth delineations for a 100 μm isotropic ex vivo hemisphere (that we use for quantitative evaluation of our segmentation method in this paper). By enabling researchers worldwide to analyse brain MRI scans at a superior level of granularity without manual effort or highly specific neuroanatomical knowledge, NextBrain holds promise to increase the specificity of MRI findings and ultimately accelerate our quest to understand the human brain in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures





 ), disadvantages (
), disadvantages ( ), and neutral points. (
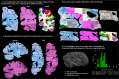
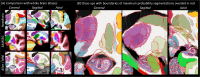
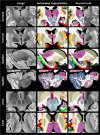
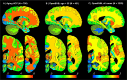
), and neutral points. ( ). (A) Printed atlas [1] with a sparse set of manually traced sections [1]. (B-G) Histological atlases of specific ROIs with limited coverage: (B) Manually traced section of basal ganglia [8]; (C) 3D rendering of deterministic thalamic atlas [11]; (D-F) Traced MRI slice, histological section, and 3D rendering of hippocampal atlas [12]; and (G) Slice of our probabilistic atlas of the thalamus [14]. (H-N) Histological atlases of the whole human brain: (H) 3D reconstructed slice of BigBrain [13]; (I) Slice of Julich-Brain labels on MNI template; (J) Labelled histological section of the Allen reference brain [7]; (K) Labelling of MNI template with protocol inspired by (J); and (L-N) MRI, histology, and 3D rendering of AHEAD brains [22]. (O-S) Our new atlas NextBrain includes dense 3D histology (O-P) and comprehensive manual labels (Q) of five specimens, enabling the construction of a probabilistic atlas (R) that can be combined with Bayesian techniques to automatically label 333 ROIs in in vivo MRI scans (S).
). (A) Printed atlas [1] with a sparse set of manually traced sections [1]. (B-G) Histological atlases of specific ROIs with limited coverage: (B) Manually traced section of basal ganglia [8]; (C) 3D rendering of deterministic thalamic atlas [11]; (D-F) Traced MRI slice, histological section, and 3D rendering of hippocampal atlas [12]; and (G) Slice of our probabilistic atlas of the thalamus [14]. (H-N) Histological atlases of the whole human brain: (H) 3D reconstructed slice of BigBrain [13]; (I) Slice of Julich-Brain labels on MNI template; (J) Labelled histological section of the Allen reference brain [7]; (K) Labelling of MNI template with protocol inspired by (J); and (L-N) MRI, histology, and 3D rendering of AHEAD brains [22]. (O-S) Our new atlas NextBrain includes dense 3D histology (O-P) and comprehensive manual labels (Q) of five specimens, enabling the construction of a probabilistic atlas (R) that can be combined with Bayesian techniques to automatically label 333 ROIs in in vivo MRI scans (S).

References
-
- Mai J. K., Majtanik M. & Paxinos G. Atlas of the human brain. (Academic Press, 2015).
-
- Dufumier B. et al. OpenBHB: a Large-Scale Multi-Site Brain MRI Data-set for Age Prediction and Debiasing. NeuroImage 263, 119637 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Atzeni A., Jansen M., Ourselin S. & Iglesias J. E. in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018: 21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, September 16–20, 2018, Proceedings, Part II11. 219–227 (Springer; ).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
