This is a preprint.
A blended genome and exome sequencing method captures genetic variation in an unbiased, high-quality, and cost-effective manner
- PMID: 39282356
- PMCID: PMC11398523
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.06.611689
A blended genome and exome sequencing method captures genetic variation in an unbiased, high-quality, and cost-effective manner
Abstract
We deployed the Blended Genome Exome (BGE), a DNA library blending approach that generates low pass whole genome (1-4× mean depth) and deep whole exome (30-40× mean depth) data in a single sequencing run. This technology is cost-effective, empowers most genomic discoveries possible with deep whole genome sequencing, and provides an unbiased method to capture the diversity of common SNP variation across the globe. To evaluate this new technology at scale, we applied BGE to sequence >53,000 samples from the Populations Underrepresented in Mental Illness Associations Studies (PUMAS) Project, which included participants across African, African American, and Latin American populations. We evaluated the accuracy of BGE imputed genotypes against raw genotype calls from the Illumina Global Screening Array. All PUMAS cohorts had concordance ≥95% among SNPs with MAF≥1%, and never fell below ≥90% for SNPs with MAF<1%. Furthermore, concordance rates among local ancestries within two recently admixed cohorts were consistent among SNPs with MAF≥1%, with only minor deviations in SNPs with MAF<1%. We also benchmarked the discovery capacity of BGE to access protein-coding copy number variants (CNVs) against deep whole genome data, finding that deletions and duplications spanning at least 3 exons had a positive predicted value of ~90%. Our results demonstrate BGE scalability and efficacy in capturing SNPs, indels, and CNVs in the human genome at 28% of the cost of deep whole-genome sequencing. BGE is poised to enhance access to genomic testing and empower genomic discoveries, particularly in underrepresented populations.
Figures

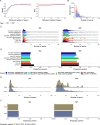

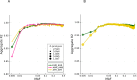
References
-
- Plenge R. M., Scolnick E. M. & Altshuler D. Validating therapeutic targets through human genetics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 12, 581–594 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 MH120642/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH137407/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH125047/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG012869/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD081256/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123451/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH125045/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113078/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH085953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH117229/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007033/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH125049/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH115676/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
