This is a preprint.
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15 antagonizes the cGAS-STING-mediated antiviral innate immune responses
- PMID: 39282446
- PMCID: PMC11398466
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.05.611469
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15 antagonizes the cGAS-STING-mediated antiviral innate immune responses
Abstract
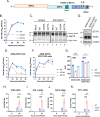
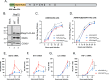
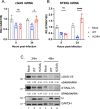
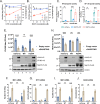
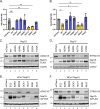
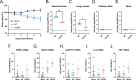
Coronavirus (CoV) Nsp15 is a viral endoribonuclease (EndoU) with a preference for uridine residues. CoV Nsp15 is an innate immune antagonist which prevents dsRNA sensor recognition and stress granule formation by targeting viral and host RNAs. SARS-CoV-2 restricts and delays the host antiviral innate immune responses through multiple viral proteins, but the role of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15 in innate immune evasion is not completely understood. Here, we generate an EndoU activity knockout rSARS-CoV-2Nsp15-H234A to elucidate the biological functions of Nsp15. Relative to wild-type rSARS-CoV-2, replication of rSARS-CoV-2Nsp15-H234A was significantly decreased in IFN-responsive A549-ACE2 cells but not in its STAT1 knockout counterpart. Transcriptomic analysis revealed upregulation of innate immune response genes in cells infected with rSARS-CoV-2Nsp15-H234A relative to wild-type virus, including cGAS-STING, cytosolic DNA sensors activated by both DNA and RNA viruses. Treatment with STING inhibitors H-151 and SN-011 rescued the attenuated phenotype of rSARS-CoV-2Nsp15-H234A. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15 inhibited cGAS-STING-mediated IFN-β promoter and NF-κB reporter activity, as well as facilitated the replication of EV-D68 and NDV by diminishing cGAS and STING expression and downstream innate immune responses. Notably, the decline in cGAS and STING was also apparent during SARS-CoV-2 infection. The EndoU activity was essential for SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15-mediated cGAS and STING downregulation, but not all HCoV Nsp15 share the consistent substrate selectivity. In the hamster model, rSARS-CoV-2Nsp15-H234A replicated to lower titers in the nasal turbinates and lungs and induced higher innate immune responses. Collectively, our findings exhibit that SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15 serves as a host innate immune antagonist by targeting host cGAS and STING.
Keywords: Biological Sciences/Microbiology; Nsp15; SARS-CoV-2; cGAS-STING; innate immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement: S.J. is a co-founder of Elucidate Bio Inc, has received speaking honorariums from Cell Signaling Technology, and has received research support from Roche unrelated to this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
