Complexities in the Diagnosis and Management of Anti-Hu Antibody-Associated Paraneoplastic Syndrome
- PMID: 39282488
- PMCID: PMC11402458
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.69457
Complexities in the Diagnosis and Management of Anti-Hu Antibody-Associated Paraneoplastic Syndrome
Abstract
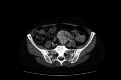
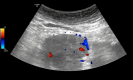
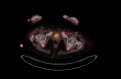
Anti-Hu is the most commonly associated antibody in paraneoplastic syndromes (PNS) - mainly secondary to small cell lung cancer (SCLC), breast cancer, thymoma, and lymphoma. This case is about a 65-year-old female patient presenting with slurred speech, headache, and loss of balance for one day. On examination, she was found to have downbeat and bilateral gaze-evoked nystagmus, dysarthria, and bilateral intention tremors. The rest of the neurological examination was unremarkable. Upon investigation, a CT scan showed a pre-sacral mass and a PET scan showed a lobulated soft tissue mesenteric mass at L5/S1, thought to possibly be a gastrointestinal stromal tumour, and mediastinal lymph nodes including right lower pre-tracheal, subcarinal and right hilar lymph nodes. Additionally, paraneoplastic antibody testing was positive for anti-Hu antibodies. She was given a five-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin without significant clinical improvement. The patient was discharged on a fast-track pathway and did not undergo chemotherapy, radiotherapy or surgical resection as the primary tumour could not be diagnosed. Paraneoplastic antibodies are a family of autoantibodies occurring as a result of malignancy that act to recognize antigens in the brain, resulting in a variety of neurological manifestations. Despite well-known literature on this entity, PNS is notoriously difficult to diagnose and manage. The first step in the management of PNS is to treat the underlying malignancy. Beyond this, the other key component of PNS treatment is immune modulation which may involve immunosuppression with high-dose corticosteroids, IV immunoglobulins, plasma exchange or plasmapheresis. It is therefore important for PNS to be diagnosed early and to adopt a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach to improve the outcomes of those presenting with PNS.
Keywords: anti-hu; intravenous immunoglobulins (ivig); mesenteric mass; paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome; presacral mass; small-cell lung carcinoma.
Copyright © 2024, Sumaruth et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Paraneoplastic syndromes associated with anti-Hu antibodies. Senties-Madrid H, Vega-Boada F. https://www.ima.org.il/MedicineIMAJ/viewarticle.aspx?year=2001&month=02&.... Isr Med Assoc J. 2001;3:94–103. - PubMed
-
- Thapa B, Mahendraker N, Ramphul K. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; Paraneoplastic syndromes. - PubMed
-
- Neuronal antinuclear antibody in sensory neuronopathy from lung cancer. Graus F, Cordon-Cardo C, Posner JB. Neurology. 1985;35:538–543. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
