The Spironolactone Initiation Registry Randomized Interventional Trial in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (SPIRRIT-HFpEF): Rationale and design
- PMID: 39282788
- PMCID: PMC11659483
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.3453
The Spironolactone Initiation Registry Randomized Interventional Trial in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (SPIRRIT-HFpEF): Rationale and design
Abstract
Aims: Benefits of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) in heart failure with preserved and mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF/HFmrEF) have not been established. Conventional randomized controlled trials are complex and expensive. The Spironolactone Initiation Registry Randomized Interventional Trial in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (SPIRRIT-HFpEF) is a unique pragmatic registry-based randomized controlled trial.
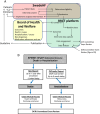
Methods: SPIRRIT-HFpEF is a multicentre, prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded endpoint trial conducted on platforms in the Swedish Heart Failure Registry (SwedeHF) and the United States (US) Trial Innovation Network. Patients with HFpEF/HFmrEF are randomized 1:1 to spironolactone (or eplerenone) in addition to usual care, versus usual care alone. The primary outcome is total number of cardiovascular deaths and hospitalizations for heart failure. Outcomes are collected from Swedish administrative complete coverage registries and a US call centre and subsequently adjudicated. Simple eligibility criteria were based on data available in SwedeHF: heart failure as outpatient or at discharge from hospital, left ventricular ejection fraction ≥40%, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide >300 ng/L (in sinus rhythm) or >750 ng/L (in atrial fibrillation), with pre-specified adjustment for elevated body mass index, and chronic loop diuretic use. Power and sample size assessments were based on an event-driven design allowing enrolment over approximately 6 years, and application of hazard ratios from the TOPCAT trial, Americas subset. The final sample size is expected to be approximately 2400 patients.
Conclusion: SPIRRIT-HFpEF will be informative on the effectiveness of generic MRAs in HFpEF and HFmrEF, and on the feasibility of conducting pragmatic and registry-based trials in heart failure and other chronic conditions.
Keywords: Aldosterone; Eplerenone; Heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction; Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists; Pragmatic trial; Registry‐based randomized clinical trial; Spironolactone.
© 2024 The Author(s). European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Bohm M, et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail 2022;24:4–131. 10.1002/ejhf.2333 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

