Adjuvant Pembrolizumab versus Observation in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma
- PMID: 39282902
- PMCID: PMC11698643
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2401726
Adjuvant Pembrolizumab versus Observation in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma is an aggressive disease with high rates of relapse. Whether pembrolizumab as adjuvant therapy would be effective in patients with high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma after radical surgery is unknown.
Methods: In this phase 3 trial, we randomly assigned patients, in a 1:1 ratio, to receive pembrolizumab at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks for 1 year or to undergo observation. Randomization was stratified according to pathological stage, centrally tested programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) status, and previous neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The coprimary end points were disease-free survival and overall survival in the intention-to-treat population. We considered the trial to be successful if either disease-free survival or overall survival was significantly longer with pembrolizumab than with observation.
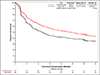
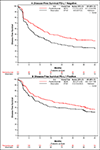
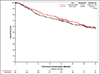
Results: A total of 702 patients underwent randomization; 354 were assigned to receive pembrolizumab, and 348 were assigned to observation. As of July 5, 2024, the median duration of follow-up for disease-free survival was 44.8 months. The median disease-free survival was 29.6 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 20.0 to 40.7) with pembrolizumab and 14.2 months (95% CI, 11.0 to 20.2) with observation (hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.90; two-sided P = 0.003). Grade 3 or higher adverse events (regardless of attribution) occurred in 50.6% of the patients in the pembrolizumab group and in 31.6% of the patients in the observation group.
Conclusions: Among patients with high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma after radical surgery, disease-free survival was significantly longer with adjuvant pembrolizumab than with observation. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health and others; Alliance A031501 AMBASSADOR ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03244384.).
Copyright © 2024 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2024. American Cancer Society. Accessed June 2024, https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts...
-
- Holzbeierlein J, Bixler BR, Buckley DI, et al. Treatment of Non-Metastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/ASCO/SUO Guideline (2017; Amended 2020, 2024). J Urol 2024;212:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Meeks JJ, Bellmunt J, Bochner BH, et al. A systematic review of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2012;62:523–33. - PubMed
-
- Pfister C, Gravis G, Fléchon A, et al. Dose-Dense Methotrexate, Vinblastine, Doxorubicin, and Cisplatin or Gemcitabine and Cisplatin as Perioperative Chemotherapy for Patients With Nonmetastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Results of the GETUG-AFU V05 VESPER Trial. J Clin Oncol 2022;40:2013–22. - PubMed
-
- Hautmann RE, de Petriconi RC, Pfeiffer C, Volkmer BG. Radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder without neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy: long-term results in 1100 patients. Eur Urol 2012;61:1039–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233247/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233253/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA BC011351/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233290/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA232760/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA239767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233327/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
