Dysregulated FOXO1 activity drives skeletal muscle intrinsic dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 39283487
- PMCID: PMC11405449
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-024-02794-y
Dysregulated FOXO1 activity drives skeletal muscle intrinsic dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
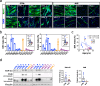
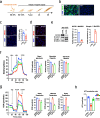
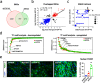
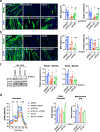
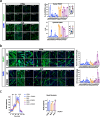
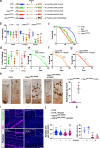
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a multisystemic neurodegenerative disorder, with accumulating evidence indicating metabolic disruptions in the skeletal muscle preceding disease symptoms, rather than them manifesting as a secondary consequence of motor neuron (MN) degeneration. Hence, energy homeostasis is deeply implicated in the complex physiopathology of ALS and skeletal muscle has emerged as a key therapeutic target. Here, we describe intrinsic abnormalities in ALS skeletal muscle, both in patient-derived muscle cells and in muscle cell lines with genetic knockdown of genes related to familial ALS, such as TARDBP (TDP-43) and FUS. We found a functional impairment of myogenesis that parallels defects of glucose oxidation in ALS muscle cells. We identified FOXO1 transcription factor as a key mediator of these metabolic and functional features in ALS muscle, via gene expression profiling and biochemical surveys in TDP-43 and FUS-silenced muscle progenitors. Strikingly, inhibition of FOXO1 mitigated the impaired myogenesis in both the genetically modified and the primary ALS myoblasts. In addition, specific in vivo conditional knockdown of TDP-43 or FUS orthologs (TBPH or caz) in Drosophila muscle precursor cells resulted in decreased innervation and profound dysfunction of motor nerve terminals and neuromuscular synapses, accompanied by motor abnormalities and reduced lifespan. Remarkably, these phenotypes were partially corrected by foxo inhibition, bolstering the potential pharmacological management of muscle intrinsic abnormalities associated with ALS. The findings demonstrate an intrinsic muscle dysfunction in ALS, which can be modulated by targeting FOXO factors, paving the way for novel therapeutic approaches that focus on the skeletal muscle as complementary target tissue.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FOXO1; FUS; Glycolysis; Myogenesis; TDP-43.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SD is a named inventor on patents related to neurological disorders. MZuf, ALM, GG, FGB, and SAM are co-inventors of patent PCT/EP2021/064274 and therefore entitled to a share of royalties. MZuf, LB, ALM, GGL, FGB, and SAM also have ownership in Miaker Developments S.L., which is the licensee of that patent related to the research being reported. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of the Basque Country and Biogipuzkoa Health Research Institute/BIOEF (representing the Basque public administration), as co-owners of the patent.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CB06/05/1126/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas
- PI2020/08-1/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas
- P18/01066/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI19/00175/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI21/00153/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI22/00433/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- IJC2019-039965-I/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- 2020-CIEN-000057-01/Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa
- 2021-CIEN-000020-01/Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa
- 2019-FELL-000010-01/Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa
- 2020-FELL-000016-02-01/Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa
- 2021-FELL-000013-02-01/Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa
- BIO17/ND/023/BD/EiTB Maratoia
- 2015111122/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- 2017222027/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- 2018111042/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- 2019222020/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- 2020111032/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- 2020333043/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- 2021333050/Osasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritzako
- PRE_2015_1_0023/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2019_1_0339/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2020_1_0122/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2020_1_0191/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2020_1_0119/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2018_1_0095/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2021_1_0125/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PRE_2018_1_0253/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- NEURODEGENPROT/Hezkuntza, Hizkuntza Politika Eta Kultura Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza
- PIF18/317/Euskal Herriko Unibertsitatea
- RYC2018-024397-I/Spanish National Plan for Scientific and Technical Research and Innovation
- RF/2019/001/Ikerbasque, Basque Foundation for Science
- RF/2023/010/Ikerbasque, Basque Foundation for Science
- PP/2022/003/Ikerbasque, Basque Foundation for Science
- BIO19/ROCHE/017/BD/Roche España
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

