Heavy rainfalls in Poland and their hyetographs
- PMID: 39283542
- PMCID: PMC11607261
- DOI: 10.1007/s13280-024-02069-6
Heavy rainfalls in Poland and their hyetographs
Abstract
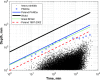
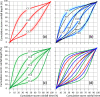
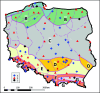
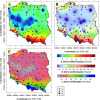
In the light of observed variability in precipitation patterns, there is a growing need for comprehensive data mining of regularly updated rainfall recording databases. Therefore, an analysis of heavy rainfall and hyetographs was conducted using a 30-year high-resolution dataset from 100 rain gauges across Poland, covering 31 646 rainfall events. Distributions of rainfall depths, durations, and intensities were explored, and maxima were compared to global records. Spatial analysis revealed significant variations in the frequency, depths, and durations of extreme rainfall across different regions. Cluster analysis determined model hyetographs for each station. The likelihood of regions belonging to clusters with three to five model hyetographs was assessed using Indicator Kriging. Findings underscore the importance of using local, characteristics rainfalls in hydrodynamic modelling of drainage systems and future rainfall scenarios. These results provide a foundational step towards understanding and monitoring the impacts of climate change on rainfall characteristics, especially extremes, in future decades.
Keywords: Classification quality assessment indices; Cluster analysis; Heavy rainfalls; Model hyetographs; Poland; Precipitation modelling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding institution had no role in the design of the study, in the samples collection, analyses, interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander, L.V., X. Zhang, T.C. Peterson, J. Caesar, B. Gleason, A.M.C. Klein Tank, M. Haylock, D. Collins, et al. 2006. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research 111: D05109. 10.1029/2005JD006290.
-
- Asadieh, B., and N.Y. Krakauer. 2015. Global trends in extreme precipitation: Climate models versus observations. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 19: 877–891. 10.5194/hess-19-877-2015.
-
- Banasik, K., ed. 2005. Wydatek i charakterystyka rumowiska unoszonego w wezbraniach opadowychz obszarów rolniczych [Suspended sediment yield in flash floods from agricultural areas]. Research report. Warsaw, Poland: Warsaw Agricultural University (in Polish).
-
- Banasik, K., ed. 2009. Modelowanie katastrofalnych wezbrań opadowych w małych zlewniach rzecznych [Modelling of the catastrophic pluvial floods in small river basins]. Research report. Warsaw, Poland: Warsaw University of Life Sciences – SGGW (in Polish).
-
- Banasik, K., and J. Ostrowski. 2010. Estimation of extreme flood flows in a small Carpathian river. In Cultural landscapes of river valleys, ed. A. Radecki-Pawlik and J. Hernik, 221–227. Krakowie: Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Rolniczego.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

