Mechanistic pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling and simulations of naloxone auto-injector 10 mg reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression
- PMID: 39283753
- PMCID: PMC11494827
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.13215
Mechanistic pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling and simulations of naloxone auto-injector 10 mg reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression
Abstract
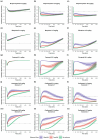
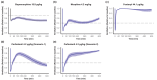
The purpose of the analysis was to evaluate if 10 mg naloxone, administered intramuscularly, could reverse or prevent opioid-induced respiratory depression (OIRD), including OIRD associated with the administration of lethal doses of high-potency opioids. A naloxone population pharmacokinetic (PK) model was generated using data from two naloxone auto-injector (NAI) clinical PK studies. Mechanistic OIRD PK-pharmacodynamic (PD) models were constructed using published data for buprenorphine, morphine, and fentanyl. Due to the lack of published carfentanil data in humans, interspecies allometric scaling methods were used to predict carfentanil PK parameters in humans. A PD model of a combined effect-compartment and receptor kinetics model with a linear relationship between ventilation and carbon dioxide was used to predict the respiratory depression induced by carfentanil. Model-based simulations were performed using the naloxone population PK model and the constructed mechanistic OIRD PK-PD models. Changes in ventilation were assessed after opioid exposure and treatment with 2 mg naloxone or one or two doses of 10 mg naloxone. A higher percentage of subjects recovered back to the rescue ventilation thresholds and/or had a faster recovery to 40% or 70% of baseline ventilation with 10 mg compared with 2 mg naloxone. A second dose of 10 mg naloxone, administered 60 min post-opioid exposure, expedited recovery to 85% of baseline ventilation and delayed time to renarcotization compared with a single dose. In addition, when 10 mg naloxone was administered at 5, 15, 30, or 60 min before fentanyl or carfentanil exposure, rapid and profound OIRD was prevented.
© 2024 The Author(s). CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Riches JR, Read RW, Black RM, Cooper NJ, Timperley CM. Analysis of clothing and urine from Moscow theatre siege casualties reveals carfentanil and remifentanil use. J Anal Toxicol. 2012;36(9):647‐656. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services . What Are Opioids? Prevent Opioid Abuse and Addiction. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/prevention/index.html. Accessed April 28, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

